Page 208 - TPM A Route to World-Class Performance
P. 208
TPMfor equipment designers and suppliers 185
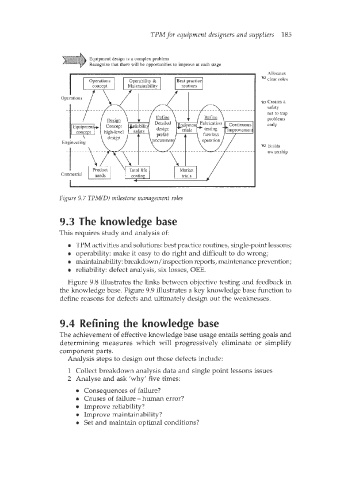
Equipment design is a complex problem
Recow that there azll be oppmtles to mprove at each stage
Allocates
R, clear roles
R) Creates a
safety
net to trap
problems
early
Builds
ownership
Figure 9.7 TPM(DI milestone management roles
9.3 The knowledge base
This requires study and analysis of:
TPM activities and solutions: best practice routines, single-point lessons;
operability: make it easy to do right and difficult to do wrong;
mainmabdity: breakdown/inspection reports, maintenance prevention;
reliability: defect analysis, six losses, OEE.
Figure 9.8 illustrates the links between objective testing and feedback in
the knowledge base. Figure 9.9 illustrates a key knowledge base function to
define reasons for defects and ultimately design out the weaknesses.
9.4 Refining the knowledge base
The achievement of effective knowledge base usage entails setting goals and
determining measures which will progressively eliminate or simplify
component parts.
Analysis steps to design out those defects include:
1 Collect breakdown analysis data and single point lessons issues
2 Analyse and ask 'why' five times:
Consequences of failure?
Causes of fdure -human error?
Improve reliability?
Improve maintainability?
Set and maintain optimal conditions?