Page 280 - Tandem Techniques
P. 280
Page 264
Hence the mobile phase largely consisted of an aqueous acetate buffer (80%) and 10% each of
acetonitrile and dioxane respectively, all three solvents being very polar in nature. In consequence, the
stationary phase had to be chosen that would retain the solutes in the presence of these very polar
solvents, and in this case the polar cyano bonded phase was employed. In fact, only a limited number of
solvents are transparent to UV at 210 nm, and if it is deemed necessary to employ light at even lower
wavelengths to monitor the separation, then this places severe restrictions on the solvents that can be
chosen for the chromatographic process.
The separation of the cardiovascular drugs was monitored with UV light at 220 nm and it is seen that a
C18 reversed phase could now be employed (a highly dispersive stationary phase) and the acetonitrile
content of the mobile phase is raised to a level of 50% at the end of the separation. At this wavelength,
the amount of solvent in the mobile phase can be higher and other solvents that are transparent at 220
nm can be used. This gives more freedom to the analyst in the choice of solvents that can be employed
to obtain the best separation. The cut-off wavelengths of a range of solvents commonly used in liquid
chromatography are shown in Table 7.1.
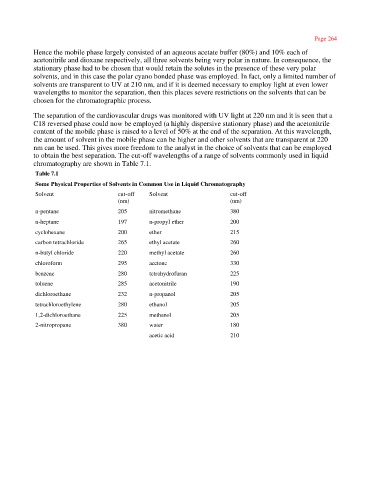
Table 7.1
Some Physical Properties of Solvents in Common Use in Liquid Chromatography
Solvent cut-off Solvent cut-off
(nm) (nm)
n-pentane 205 nitromethane 380
n-heptane 197 n-propyl ether 200
cyclohexane 200 ether 215
carbon tetrachloride 265 ethyl acetate 260
n-butyl chloride 220 methyl acetate 260
chloroform 295 acetone 330
benzene 280 tetrahydrofuran 225
toluene 285 acetonitrile 190
dichloroethane 232 n-propanol 205
tetrachloroethylene 280 ethanol 205
1,2-dichloroethane 225 methanol 205
2-nitropropane 380 water 180
acetic acid 210