Page 438 - Tandem Techniques
P. 438
Page 421
arsenic. Another example of the use of the LC/ICP-AAS tandem arrangement for the determination of
arsenic and selenium is afforded by the work of LaFrenier et al. [24], who used a direct injection
nebulizer to infuse the column eluent from a liquid chromatograph into a ICP atomic spectrometer.
They used a standard ICP torch, manufactured by Plasma-Therm. Inc., driven by a Model HFS-5000D:
27.12 MHz generator. The monochromator was the McPherson Model 2051, and the spray system was
the direct injection nebulizer, manufactured by Ames Laboratory Inc. The nebulizer flow rate was 200
ml/ min., and the auxiliary argon flow 600 ml/min. An example of a separation obtained by the authors
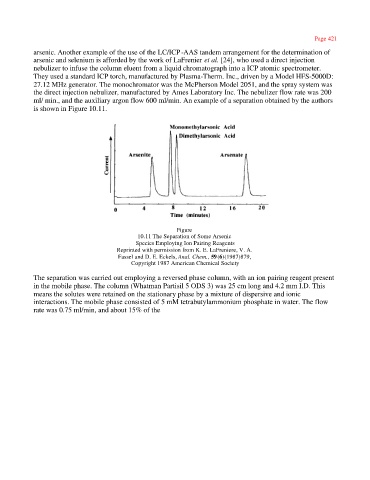
is shown in Figure 10.11.
Figure
10.11 The Separation of Some Arsenic
Species Employing Ion Pairing Reagents
Reprinted with permission from K. E. LaFreniere, V. A.
Fassel and D. E. Eckels, Anal. Chem., 59(6)(1987)879,
Copyright 1987 American Chemical Society
The separation was carried out employing a reversed phase column, with an ion pairing reagent present
in the mobile phase. The column (Whatman Partisil 5 ODS 3) was 25 cm long and 4.2 mm I.D. This
means the solutes were retained on the stationary phase by a mixture of dispersive and ionic
interactions. The mobile phase consisted of 5 mM tetrabutylammonium phosphate in water. The flow
rate was 0.75 ml/min, and about 15% of the