Page 445 - Tandem Techniques
P. 445
Page 428
appreciable concentrations of arsenic in a variety of marine organisms has stimulated still further
interest in the development of arsenic assays. The electrothermal [28] and cool diffusion flame [29, 30]
quartz nebulizers are several orders more sensitive to arsenic than the conventional flame-AAS
atomizers. However, these atomizers are restricted to the analysis of arsenic compounds that can form
volatile hydride derivatives.
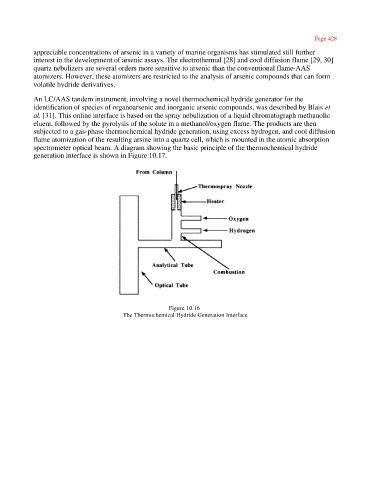
An LC/AAS tandem instrument, involving a novel thermochemical hydride generator for the
identification of species of organoarsenic and inorganic arsenic compounds, was described by Blais et
al. [31]. This online interface is based on the spray nebulization of a liquid chromatograph methanolic
eluent, followed by the pyrolysis of the solute in a methanol/oxygen flame. The products are then
subjected to a gas-phase thermochemical hydride generation, using excess hydrogen, and cool diffusion
flame atomization of the resulting arsine into a quartz cell, which is mounted in the atomic absorption
spectrometer optical beam. A diagram showing the basic principle of the thermochemical hydride
generation interface is shown in Figure 10.17.
Figure 10.16
The Thermochemical Hydride Generation Interface