Page 91 - Tandem Techniques
P. 91
Page 72
Raman Spectroscopy Instrumentation
The modern Raman spectrometer is based on the use of a laser light source and a FTIR spectrometer.
The laser light source must generate light of a suitable wavelength that does not produce significant
fluorescence and consequently, the excitation wavelength is chosen to be about 1 micron. A diagram of
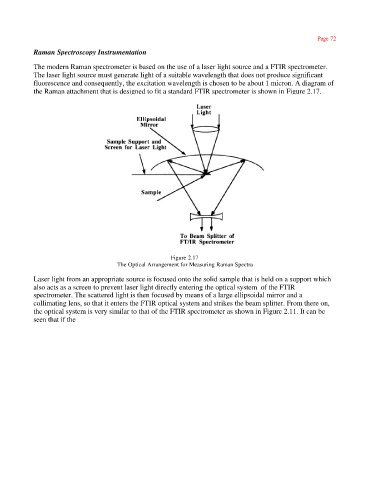
the Raman attachment that is designed to fit a standard FTIR spectrometer is shown in Figure 2.17.
Figure 2.17
The Optical Arrangement for Measuring Raman Spectra
Laser light from an appropriate source is focused onto the solid sample that is held on a support which
also acts as a screen to prevent laser light directly entering the optical system of the FTIR
spectrometer. The scattered light is then focused by means of a large ellipsoidal mirror and a
collimating lens, so that it enters the FTIR optical system and strikes the beam splitter. From there on,
the optical system is very similar to that of the FTIR spectrometer as shown in Figure 2.11. It can be
seen that if the