Page 95 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 95
15:32
March 9, 2004
Char Count= 0
WU095/Kulaev
WU095-06
Enzymes of polyphosphate degradation 79
enzyme active centers contained no SH groups necessary for the activity. Insensitivity of
all exopolyphosphatases types to orthovanadate suggests their inability to form a phospho-
rylated intermediate during the PolyP hydrolysis reaction.
It should be noted that, in spite of the solubilities of most yeast exopolyphosphatases,
the detergent ‘Triton X-100’ was the best stabilizer of these enzymes during purification
and storage (Andreeva et al., 1990; Andreeva et al., 1998a,b).
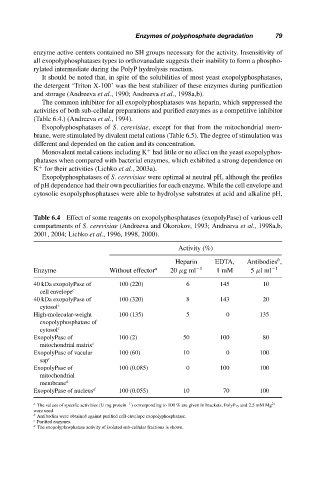
The common inhibitor for all exopolyphosphatases was heparin, which suppressed the
activities of both sub-cellular preparations and purified enzymes as a competitive inhibitor
(Table 6.4.) (Andreeva et al., 1994).
Exopolyphosphatases of S. cerevisiae, except for that from the mitochondrial mem-
brane, were stimulated by divalent metal cations (Table 6.5). The degree of stimulation was
different and depended on the cation and its concentration.
Monovalent metal cations including K had little or no effect on the yeast exopolyphos-
+
phatases when compared with bacterial enzymes, which exhibited a strong dependence on
K for their activities (Lichko et al., 2003a).
+
Exopolyphosphatases of S. cerevisiae were optimal at neutral pH, although the profiles
of pH dependence had their own peculiarities for each enzyme. While the cell envelope and
cytosolic exopolyphosphatases were able to hydrolyse substrates at acid and alkaline pH,
Table 6.4 Effect of some reagents on exopolyphosphatases (exopolyPase) of various cell
compartments of S. cerevisiae (Andreeva and Okorokov, 1993; Andreeva et al., 1998a,b,
2001, 2004; Lichko et al., 1996, 1998, 2000).
Activity (%)
b
Heparin EDTA, Antibodies ,
Enzyme Without effector a 20 µgml −1 1mM 5 µlml −1
40 kDa exopolyPase of 100 (220) 6 145 10
cell envelope c
40 kDa exopolyPase of 100 (320) 8 143 20
cytosol c
High-molecular-weight 100 (135) 5 0 135
exopolyphosphatase of
cytosol c
ExopolyPase of 100 (2) 50 100 80
mitochondrial matrix c
ExopolyPase of vacular 100 (60) 10 0 100
sap c
ExopolyPase of 100 (0.085) 0 100 100
mitochondrial
membrane d
ExopolyPase of nucleus d 100 (0.055) 10 70 100
−1
a The values of specific activities (U mg protein ) corresponding to 100 % are given in brackets. PolyP 15 and 2.5 mM Mg 2+
were used.
b Antibodies were obtained against purified cell-envelope exopolyphosphatase.
c Purified enzymes.
d
The exopolyphosphatase activity of isolated sub-cellular fractions is shown.