Page 138 - The Combined Finite-Discrete Element Method
P. 138
GENERALISATION OF MUNJIZA-NBS CONTACT DETECTION ALGORITHM 121
y
x
z
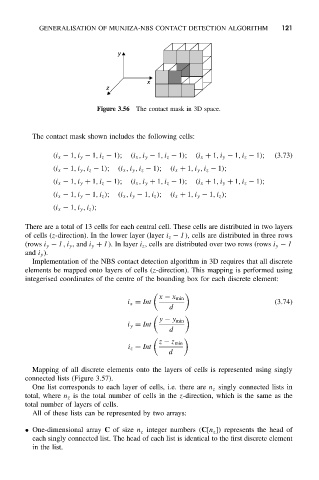
Figure 3.56 The contact mask in 3D space.
The contact mask shown includes the following cells:
(i x − 1,i y − 1,i z − 1); (i x ,i y − 1,i z − 1); (i x + 1,i y − 1,i z − 1); (3.73)
(i x − 1,i y ,i z − 1); (i x ,i y ,i z − 1); (i x + 1,i y ,i z − 1);
(i x − 1,i y + 1,i z − 1); (i x ,i y + 1,i z − 1); (i x + 1,i y + 1,i z − 1);
(i x − 1,i y − 1,i z ); (i x ,i y − 1,i z ); (i x + 1,i y − 1,i z );
(i x − 1,i y ,i z );
There are a total of 13 cells for each central cell. These cells are distributed in two layers
of cells (z-direction). In the lower layer (layer i z − 1), cells are distributed in three rows
(rows i y − 1,i y ,and i y + 1). In layer i z , cells are distributed over two rows (rows i y − 1
and i y ).
Implementation of the NBS contact detection algorithm in 3D requires that all discrete
elements be mapped onto layers of cells (z-direction). This mapping is performed using
integerised coordinates of the centre of the bounding box for each discrete element:
x − x min
i x = Int (3.74)
d
y − y min
i y = Int
d
z − z min
i z = Int
d
Mapping of all discrete elements onto the layers of cells is represented using singly
connected lists (Figure 3.57).
One list corresponds to each layer of cells, i.e. there are n z singly connected lists in
total, where n z is the total number of cells in the z-direction, which is the same as the
total number of layers of cells.
All of these lists can be represented by two arrays:
• One-dimensional array C of size n z integer numbers (C[n z ]) represents the head of
each singly connected list. The head of each list is identical to the first discrete element
in the list.