Page 146 - The Combined Finite-Discrete Element Method
P. 146
SHAPE AND SIZE GENERALISATION–WILLIAMS C-GRID ALGORITHM 129
In
Out
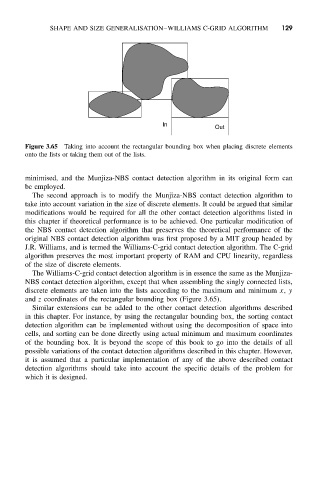
Figure 3.65 Taking into account the rectangular bounding box when placing discrete elements
onto the lists or taking them out of the lists.
minimised, and the Munjiza-NBS contact detection algorithm in its original form can
be employed.
The second approach is to modify the Munjiza-NBS contact detection algorithm to
take into account variation in the size of discrete elements. It could be argued that similar
modifications would be required for all the other contact detection algorithms listed in
this chapter if theoretical performance is to be achieved. One particular modification of
the NBS contact detection algorithm that preserves the theoretical performance of the
original NBS contact detection algorithm was first proposed by a MIT group headed by
J.R. Williams, and is termed the Williams-C-grid contact detection algorithm. The C-grid
algorithm preserves the most important property of RAM and CPU linearity, regardless
of the size of discrete elements.
The Williams-C-grid contact detection algorithm is in essence the same as the Munjiza-
NBS contact detection algorithm, except that when assembling the singly connected lists,
discrete elements are taken into the lists according to the maximum and minimum x, y
and z coordinates of the rectangular bounding box (Figure 3.65).
Similar extensions can be added to the other contact detection algorithms described
in this chapter. For instance, by using the rectangular bounding box, the sorting contact
detection algorithm can be implemented without using the decomposition of space into
cells, and sorting can be done directly using actual minimum and maximum coordinates
of the bounding box. It is beyond the scope of this book to go into the details of all
possible variations of the contact detection algorithms described in this chapter. However,
it is assumed that a particular implementation of any of the above described contact
detection algorithms should take into account the specific details of the problem for
which it is designed.