Page 148 - The Combined Finite-Discrete Element Method
P. 148
4
Deformability of Discrete
Elements
4.1 DEFORMATION
Discrete elements were originally introduced to model problems and processes that
continuum-based models cannot model correctly. A large class of such problems and
processes are generally termed ‘problems of discontinua’. However, a large class
of problems of discontinua involves individual bodies (discrete elements) that can
deform, fail, fracture and even fragment. Such discrete elements are termed ‘deformable
discrete elements’.
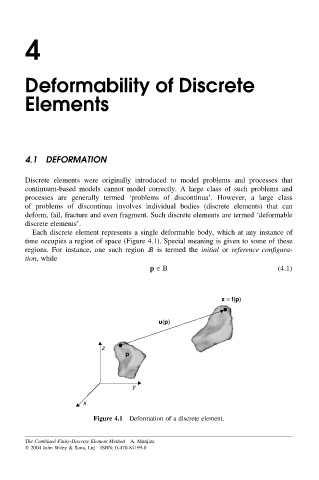
Each discrete element represents a single deformable body, which at any instance of
time occupies a region of space (Figure 4.1). Special meaning is given to some of these
regions. For instance, one such region B is termed the initial or reference configura-
tion, while
p ∈ B (4.1)
x = f(p)
u(p)
z
p
y
x
Figure 4.1 Deformation of a discrete element.
The Combined Finite-Discrete Element Method A. Munjiza
2004 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBN: 0-470-84199-0