Page 77 - The Combined Finite-Discrete Element Method
P. 77
60 PROCESSING OF CONTACT INTERACTION
3
4
1
2
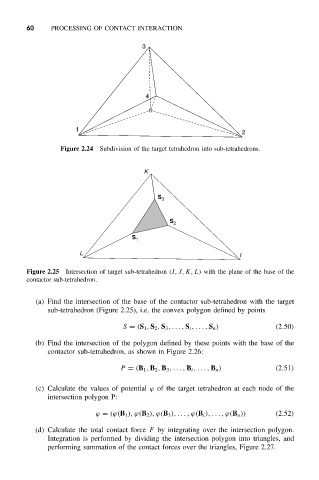
Figure 2.24 Subdivision of the target tetrahedron into sub-tetrahedrons.
K
S 3
S 2
S 1
L I
Figure 2.25 Intersection of target sub-tetrahedron (I,J,K,L) with the plane of the base of the
contactor sub-tetrahedron.
(a) Find the intersection of the base of the contactor sub-tetrahedron with the target
sub-tetrahedron (Figure 2.25), i.e. the convex polygon defined by points
S = (S 1 , S 2 , S 3 ,..., S i ,. .., S n ) (2.50)
(b) Find the intersection of the polygon defined by these points with the base of the
contactor sub-tetrahedron, as shown in Figure 2.26:
P = (B 1 , B 2 , B 3 ,..., B i ,. .., B n ) (2.51)
(c) Calculate the values of potential ϕ of the target tetrahedron at each node of the
intersection polygon P:
ϕ = (ϕ(B 1 ), ϕ(B 2 ), ϕ(B 3 ), ... ,ϕ(B i ), ...,ϕ(B n )) (2.52)
(d) Calculate the total contact force F by integrating over the intersection polygon.
Integration is performed by dividing the intersection polygon into triangles, and
performing summation of the contact forces over the triangles, Figure 2.27.