Page 291 - Bruce Ellig - The Complete Guide to Executive Compensation (2007)
P. 291
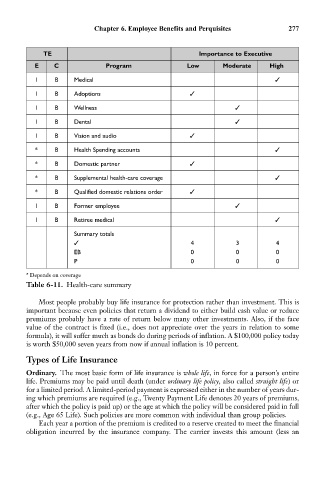
Chapter 6. Employee Benefits and Perquisites 277
TE Importance to Executive
E C Program Low Moderate High
1 B Medical
1 B Adoptions
1 B Wellness
1 B Dental
1 B Vision and audio
* B Health Spending accounts
* B Domestic partner
* B Supplemental health-care coverage
* B Qualified domestic relations order
1 B Former employee
1 B Retiree medical
Summary totals
4 3 4
EB 0 0 0
P 0 0 0
* Depends on coverage
Table 6-11. Health-care summary
Most people probably buy life insurance for protection rather than investment. This is
important because even policies that return a dividend to either build cash value or reduce
premiums probably have a rate of return below many other investments. Also, if the face
value of the contract is fixed (i.e., does not appreciate over the years in relation to some
formula), it will suffer much as bonds do during periods of inflation. A $100,000 policy today
is worth $50,000 seven years from now if annual inflation is 10 percent.
Types of Life Insurance
Ordinary. The most basic form of life insurance is whole life, in force for a person’s entire
life. Premiums may be paid until death (under ordinary life policy, also called straight life) or
for a limited period. A limited-period payment is expressed either in the number of years dur-
ing which premiums are required (e.g., Twenty Payment Life denotes 20 years of premiums,
after which the policy is paid up) or the age at which the policy will be considered paid in full
(e.g., Age 65 Life). Such policies are more common with individual than group policies.
Each year a portion of the premium is credited to a reserve created to meet the financial
obligation incurred by the insurance company. The carrier invests this amount (less an