Page 120 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 120
Rolling bearing materia Is A21
COMPOSTION AND PROPERTIES
The stress levels in rolling bearings limit the choice of amongst the requirements and also because of economic
materials to those with a high vield and high creep strength. considerations. The through hardening steels are listed
In addition, there are a number of other important con- in Table 21.1. The 535 grade is most popular (formerly
siderations in the selection of suitable materials, including EN31), but is not satisfactory at elevated temperatures
the following : due to loss of hardness and fatigue resistance. High-speed
High impact strength tool steels containing principally tungsten and rnolybde-
Good wear resistance num are superior to other materials at elevated tempera-
Corrosion resistance tures, assuming adequate lubrication. Heat treatment is
Dimensional stability very important to give a satisfactory carbide structure of
High endurance under fatigue loading optimum hardness in order to achieve the maximum rolling
Uniformity of structure contact fatigue life. Steelmaking practice can also in-
fluence results, e.g. refinements which improve mechanical
Steels have gained the widest acceptance as rolling properties and increase resistance to failure are vacuum
contact materials as they represent the best compromise melting and modification.
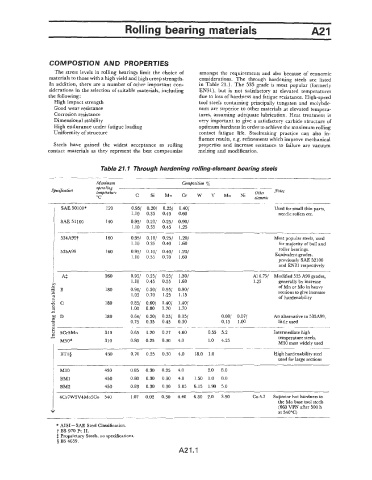
Table 21. I Through hardening rolling-element bearing steels
-
Maximum Composition %
operating -
Specification temperature Cr Other Notes
"C C Si Mn W V Mo Ni
SAE 50100* 120 0.951 0.201 0.251 0.401 Used for small thin parts,
1.10 0.35 0.45 0.60 needle rollers etc.
SAE 51 100 140 0.951 0.201 0.251 0.901
1.10 0.35 0.45 1.25
534A99f 160 0.951 0.101 0.251 1.201 Most popular steels, used
1.10 0.35 0.40 1.60 for majority of ball and
roller bearings.
535A99 160 0.951 0. lo/ 0.401 1.201 Equivalent grades,
1.10 0.35 0.70 I .60 previously SAE 52100
and EN31 respectively
i 260 0.951 0.251 0.251 1.301 A1 0.751 Modified 535 A99 grades,
i? 1.10 0.45 0.55 1.60 1.25 generally by increase
of Mn or Mo in heavy
3 B 180 0.90/ 0.501 0.951 0.901 sections to give increase
2 1.05 0.70 1.25 1.15 of hardenability
z 180 0.851 0.601 1 .a/
c
"c
1.401
1 .oo
s 0.80 1.70 1.70
.- FfD 180 0.641 0.201 0.251 0.151 0.081 0.071 An alternative to 5351499,
0.30
1.00
little used
0.15
g 0.75 0.35 0.45
8 5Cr5Mo 310 0.65 1.20 0.27 4.60 0.55 5.2 Intermediate high
temperature steels.
7 M50* 310 0.80 0.25 0.30 4.0 1.0 4.25 M50 most widely used
BT1$ 430 0.70 0.25 0.30 4.0 18.0 1.0 High hardenability steel
used for large sections
MI0 430 0.85 0.30 0.25 4.0 2.0 8.0
BMl 450 0.80 0.30 0.30 4.0 1.50 1.0 8.0
450 0.83 0.30 0.30 3.85 6.15 1.90 5.0
* AISI-SAE Steel Classification.
t BS 970 Pt 11.
$ Proprietary Steels, no specifications.
5 BS 4659.
A21.1