Page 243 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 243
B17 Piston rings
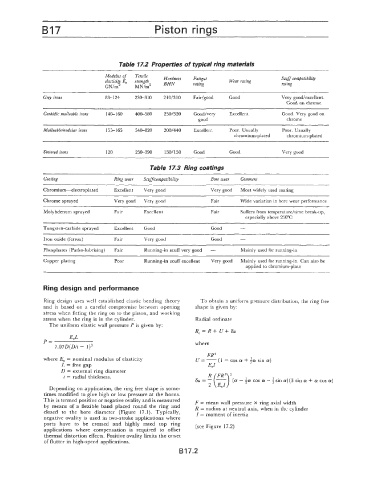
Table 17.2 Properties of typical ring materials
Modulus of Tenrile Scuff compatibili&
elasticit E,, strength Hardness Fatigue Wear rating rating
rating
BHN
GN/m ' MN/m2
Grey irons 83-124 230-310 210/310 Fair/good Good Very good/excellent.
Good on chrome
Carbidic malleable irom 140-160 400-580 250/320 Good/very Excellent Good. Very good on
good chrome
Malleable/nodular irons 155-165 540-820 200/440 Excellent Poor. Usually Poor. Usually
chromium-plated chromium-plated
Sintered irons 120 250-390 130/150 Good Good Very good
Table 17.3 Ring coatings
Coating Ring wear Scuff/compatibiSty Bore wear Comment
~~~~~ ~~
Chromium-electroplated Excellent Very good Very good Most widely used coating
Chrome sprayed Very good Very good Fair Wide variation in bore wear performance
Molybdenum sprayed Fair Excellent Fair Suffers from ternperature/time break-up,
especially above 250°C
Tungsten-carbide sprayed Excellent Good Good -
Iron oxide (ferrox) Fair Very good Good -
Phosphates (Parko-lubrising) Fair Running-in scuff very good - Mainly used for running-in
~ ~ ~~
Copper plating Poor Running-in scuff excellent Very good Mainly used for running-in. Can also be
applied to chromium-plate
Ring design and performance
Ring design uses well established elastic bending theory To obtain a uniform pressure distribution, the ring free
and is based on a careful compromise between opening shape is given by:
stress when fitting the ring on to the piston, and working
stress when the ring is in the cylinder. Radial ordinate
The uniform elastic wall pressure P is given by:
R,=R+U+Su
E,L
P= where
7.07D(D/t - 1)3
where E,, = nominal modulus of elasticity
L = free gap
D = external ring diameter
t = radial thickness.
(a - ;a cos a - 4 sin a)(3 sin a + a cos a)
Depending on application, the ring free shape is some-
times modified to eive high or low uressure at the horns.
"
v
This is termed positive or negative ovality and is measured = mean wall pressure ring axial width
by means of a flexible band placed round the ring and R = radius at neutral axis, when in the cylinder
closed to the bore diameter (Figure 17.1). Typically, I = moment of inertia
__
negative ovality is used in two-stroke applications where
poits have to- be crossed and highly rated top ring (see Figure 17.2)
applications where compensation is required to offset
thermal distortion effects. Positive ovality limits the onset
of flutter in high-speed applications.
817.2