Page 251 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 251
E318 Winders and liners
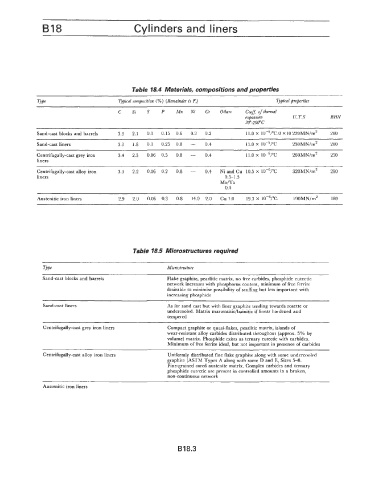
Table 18.4 Materials, compositions and properties
Type Typical composition (Yo) (Remainder is Fe) Typical properties
C Si S P Mn Ni Cr Others Coeff. of thermal
expansion U. T.S BHN
20"-200"c
Sand-cast blocks and barrels 3.3 2.1 0.1 0.15 0.6 0.3 0.2 11.0 X 10-6/oC.0 X 10 220MN/m2 200
Sand-cast liners 3.3 1.8 0.1 0.25 0.8 - 0.4 11.0 x 10-6/0c 230MN/m2 200
~ ~ ~~~~
Centrifugally-cast grey iron 3.4 2.3 0.06 0.5 08 - 0.4 11.0 x 10-6/"c 260MN/m2 250
liners
Centrifugally-cast alloy iron 3.3 2.2 0.06 0.2 0.8 - 0.4 Ni and Cu 10.5 X 10-6/oC 320MN/m2 280
liners 0.5-1.5
MoIVa
0.4
Austenitic iron liners 2.9 2.0 0.06 0.3 0.8 14.0 2.0 Cu 7.0 19.3 X 10-6/"C 190MN/m2 180
Table 18.5 Microstructures required
Trpe Microstructure
Sand-cast blocks and barrels Flake graphite, pearlitic matrix, no free carbides, phosphide eutectic
network increases with phosphorus content, minimum of free ferrite
desirable to minimise possibility of scuffing but less important with
increasing phosphide
Sand-cast liners As for sand cast but with finer graphite tending towards rosette or
undercooled. Matrix martensitic/bainitic if linear hardened and
tempered
Centrifugally-cast grey iron liners Compact graphite or quasi-flakes, pearlitic matrix, islands of
wear-resistant alloy carbides distributed throughout (approx. 5% by
volume) matrix. Phosphide exists as ternary eutectic with carbides.
Minimum of free ferrite ideal, but not important in presence of carbides
~ ~~~~
Centrifugally-cast alloy iron liners Uniformly distributed fine flake graphite along with some undercooled
graphite (ASTM Types A along with some D and E, Sizes 5-8.
Fine-grained cored austenite matrix. Complex carbides and ternary
phosphide eutectic are present in controlled amounts in a broken,
non-continuous network
Austenitic iron liners
B18.3