Page 252 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 252
Selection of seals B19
BASIC SEAL TYPES AND THEIR CHARACTERISTICS
Dynamic seal
Sealing takes place between surfaces in sliding contact or narrowly separated.
Static seal1
Sealing takes place between surfaces which do not move relative to each other.
Pseudo-static seal
Limited relative motion is possible at the sealing surfaces, or the seal itself allows limited motion; e.g. swivel couplings for
pipes, flexible diaphragms.
Exclusion seal
A device to restrict access of dirt, etc., to a system, often used in conjunction with a dynamic seal.
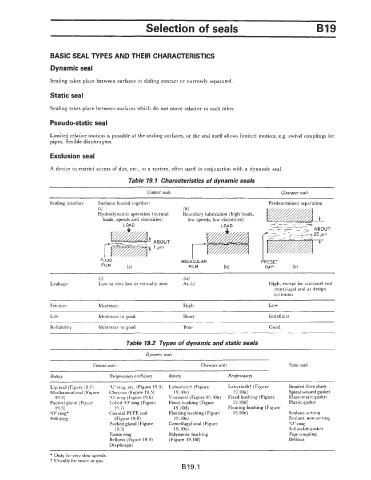
Table 19.1 Characteristics of dynamic seals
Contact seals Clearance seals
Sealing interface Surfaces loaded together: Predetermined separation
(i) (ii)
Hydrodynamic operation (normal Boundary lubrication (high loads,
loads, speeds and viscosities) low speeds, low viscosities)
LOAD
I
FLUID MOLECULAR PRESET
FILM b)
(a) FILM (b) GAP
6) (ii)
Leakage Low to very low or virtually zero As (i) High, except for viscoseal and
centrifugal seal at design
optimum
-
Friction Moderate High Low
Life Moderate to good Short Indefinite
~~ ~~
Reliability Moderate to good Poor Good
Table 19.2 Types of dynamic and static seals
Dynamic seals
Contact seals Clearance seals Static seals
Rotary RecipracatoT oscillatory Rotary Reciprocatory
Lip seal (Figure 19.1) ‘U’ ring, etc. (Figure 19.4) Labyrintht (Figure Labyrinth7 (Figure Bonded fibre sheet
Mechanical seal (Figure Chevron (Figure 19.5) 19.10a) 19.10a) Spiral wound gasket
19.2) ‘0’ ring (Figure 19.6) Viscoseal (Figure 19.10b) Fixed bushing (Figure Elastomeric gasket
Packed gland (Figure Lobed ‘0’ ring (Figure Fixed bushing (Figure 19.10d) Piastic gasket
19.3) 19.7) 19.lOd) Floating bushing (Figure
‘0’ ring* Coaxial PTFE seal Floating bushing (Figure 19. l0e) Sealant, setting
Felt ring (Figure 19.8) 19.10e) Sealant, non-setting
Packed gland (Figure Centrifugal seal (Figure ‘0’ ring
19.3) 19.1Oc) Inflatable gasket
Piston ring Polymeric bushing Pipe coupling
Bellows (Figure 19.9) (Figure 19.101) Bellows
Diaphragm
* Only for very slow speeds.
t Usually for steam or gas.
B19.1