Page 64 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 64
High speed bearings and rotor dynamics A10
Shaft lateral vibrations which may occur on machines with high speed rotors
Type of vibration Cause of the vibration Remarks
A vibration at the same frequency as the Unbalance of the rotor Can be reduced by improving the dynamic
shaft rotation which tends to increase balance of the rotor
with speed
A vibration at the same frequency as the The rotor, as supported in the machine, The response of the rotor in terms of
shaft rotation which increases in is laterally flexible and has a natural vibration amplitude will depend on a
amplitude around a particular speed lateral resonance or critical speed at balance between the damping in the
which the vibration amplitude is a system and the degree of rotor unbalance
maximum
A vibration with a frequency ofjust less The rotor is supported in lightly loaded An increase in the specific bearing loading
than half the shaft rotational speed plain journal bearings which can by a reduction in bearing width can help.
which occurs over a range of speeds generate half speed vibration (see Fig. Alternatively bearings with special bore
10.2). The actual frequency is profiles can be used (see Fig. 10.3)
generally just less than half shaft speed
due to damping
A vibration with a frequency of about The rotor is supported in lightly loaded This severe vibration arises from an
half the shaft rotational speed, which plain journal bearings and is reaching interaction between the bearings and the
shows a major increase in amplitude a rotational speed, equal to twice its rotor. The critical speed of the rotor
above a particular speed critical speed, when the major resonates with half speed vibration of the
vibration increase occurs bearings
Machines with plain journal bearings
generally have a maximum safe operating
speed of twice their first critical speed
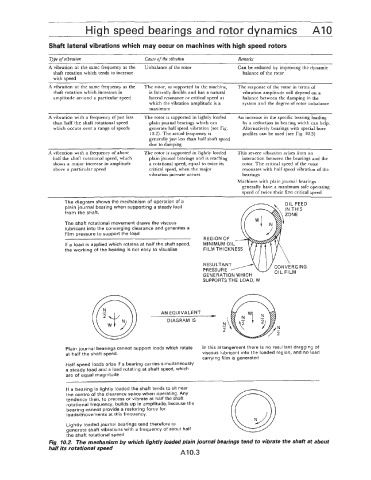
The diagram shows the mechanism of operation of a
plain journal bearing when supporting a steady load
from the shaft.
The shaft rotational movement draws the viscous
lubricant into the converging clearance and generates a
film pressure to support the load
REGION OF
If a load is applied which rotates at half the shaft speed, MINIMUM OIL
the working of the bearing is not easy to visualise FILM THICKNESS
\
RESULTANT~~JJ' CONVERGING
PRESSUR E OIL FILM
GENERATION WHICH
SUPPORTS THE LOAD, W
AN EQUIVALENT
P
DIAGRAM IS
N
- N
2 -
2
Plain journal bearings cannot support loads which rotate In this arrangement there is no resultant dragging of
at half the shaft speed. viscous lubricant into the loaded region, and no load
carrying film is generated
Half speed loads arise il a bearing carries simultaneously
a steady load and a load rotating at shaft speed, which
are of equal magnitude
If a bearing is lightly loaded the shaft tends to sit near
the centre of the clearance space when operating. Any
tendency then, to precess or vibrate at half the shaft
rotational frequency, builds up in amplitude, because the
bearing cannot provide a restoring force for
loadshnovements at this frequency.
Lightly loaded journal bearings tend therefore to
generate shaft vibrationis with a frequency of about half
the shaft rotational speed
Fig. 10.2. The mechanism by which lightly loaded plain journal bearings tend to vibrate the shaft at about
half its rotational speed
AI 0.3