Page 65 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 65
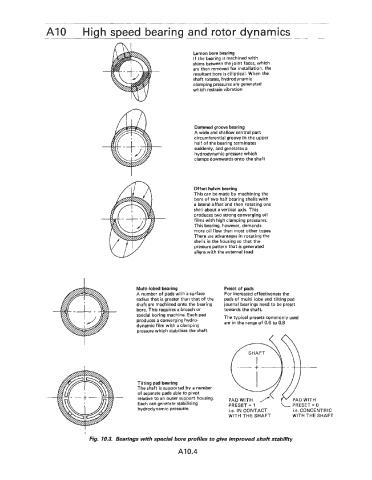
AI0 High speed bearing and rotor dynamics
Lemon bore bearing
If the bearing is machined with
shims between the joint faces, which
are then removed for installation, the
resultant bore is elliptical. When the
shaft rotates, hydrodynamic
clamping pressures are generated
which restrain vibration
Dammed groove bearing
A wide and shallow central part
circumferential groove in the upper
half of the bearing terminates
suddenly, and generates a
hydrodynamic pressure which
clamps downwards onto the shaft
Offset halves bearing
This can be made by machining the
bore of two half bearing shells with
a lateral offset and then rotating one
shell about a vertical axis. This
produces two strong converging oil
films with high clamping pressures.
This bearing, however, demands
more oil flow than most other types.
There are advantages in rotating the
shells in the housing so that the
pressure pattern that is generated
aligns with the external load
Multi-lobed bearing Preset of pads
A number of pads with a surface For increased effectiveness the
radius that is greater than that of the pads of multi lobe and tilting pad
shaft are machined onto the bearing journal bearings need to be preset
bore. This requires a broach or towards the shaft.
special boring machine. Each pad The typical presets commonly used
produces a converging hydro- are in the range of 0.6 to 0.8
dynamic film with a clamping
pressure which stabilises the shaft
Tilting pad bearing
The shaft is supported by a number
of separate pads able to pivot
relative to an outer support housing.
Each can generate stabilising
hydrodynamic pressures i.e. IN CONTACT i.e. CONCENTRIC
WITH THE SHAFT WITH THE SHAFT
Fig. 10.3. Bearings with special bore profiles to give improved shaft stability
A10.4