Page 133 - Welding of Aluminium and its Alloys
P. 133
118 The welding of aluminium and its alloys
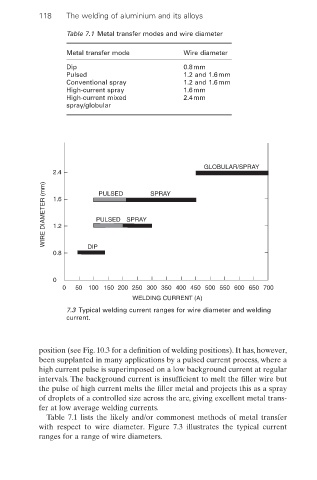
Table 7.1 Metal transfer modes and wire diameter
Metal transfer mode Wire diameter
Dip 0.8mm
Pulsed 1.2 and 1.6mm
Conventional spray 1.2 and 1.6mm
High-current spray 1.6mm
High-current mixed 2.4mm
spray/globular
GLOBULAR/SPRAY
2.4
WIRE DIAMETER (mm) 1.6 PULSED SPRAY SPRAY
PULSED
1.2
0.8 DIP
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700
WELDING CURRENT (A)
7.3 Typical welding current ranges for wire diameter and welding
current.
position (see Fig. 10.3 for a definition of welding positions). It has, however,
been supplanted in many applications by a pulsed current process, where a
high current pulse is superimposed on a low background current at regular
intervals. The background current is insufficient to melt the filler wire but
the pulse of high current melts the filler metal and projects this as a spray
of droplets of a controlled size across the arc, giving excellent metal trans-
fer at low average welding currents.
Table 7.1 lists the likely and/or commonest methods of metal transfer
with respect to wire diameter. Figure 7.3 illustrates the typical current
ranges for a range of wire diameters.