Page 210 - Theory and Design of Air Cushion Craft
P. 210
Water surface deformation in ACV air cushion 193
0.75 -
0.50
=-0.5
0.25
-0.25 ^
-0.50 -
-0.75 -
0.1
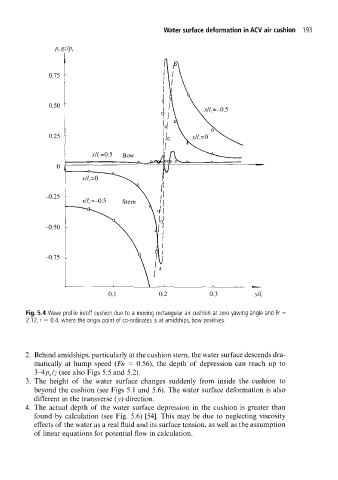
Fig. 5.4 Wave profile in/off cushion due to a moving rectangular air cushion at zero yawing angle and Fr
2.12, r = 0.4, where the origin point of co-ordinates is at amidships, bow positives.
2. Behind amidships, particularly at the cushion stern, the water surface descends dra-
matically at hump speed (Fn = 0.56), the depth of depression can reach up to
3-4/? c/}> (see also Figs 5.5 and 5.2).
3. The height of the water surface changes suddenly from inside the cushion to
beyond the cushion (see Figs 5.1 and 5.6). The water surface deformation is also
different in the transverse (y) direction.
4. The actual depth of the water surface depression in the cushion is greater than
found by calculation (see Fig. 5.6) [54]. This may be due to neglecting viscosity
effects of the water as a real fluid and its surface tension, as well as the assumption
of linear equations for potential flow in calculation.