Page 141 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 141
138 Chapter 7 Thermodynamics of the Binding of Ligands by Proteins
2
1.5 -
I -
05 -
1
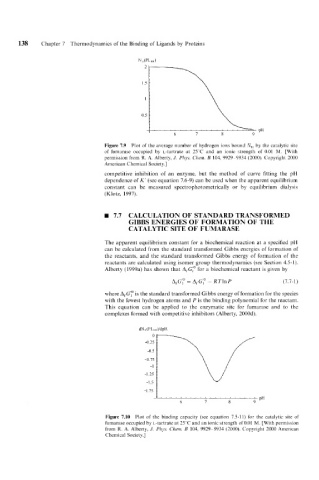
Figure 7.9 Plot of the average number of hydrogen ions bound nk, the catalytic site
by
of fumarase occupicd by L-tartrate at 25'C and an ionic strength of 0.01 M. [With
permission from R. A. Alberty, J. Phys. C'hcm. B 104, 9929-9934 (2000). Copyright 2000
American Chemical Society.]
competitive inhibition of an enzyme, but the method of curve fitting the pH
dependence of K' (see equation 7.6-9) can be used when the apparent equilibrium
constant can be measured spectrophotometrically or by equilibrium dialysis
(Klotz, 1997).
rn 7.7 CALCULATION OF STANDARD TRANSFORMED
GIBBS ENERGIES OF FORMATION OF THE
CATALYTIC SITE OF FUMARASE
The apparent equilibrium constant for a biochemical reaction at a specified pH
can be calculated from the standard transformed Gibbs energies of formation of
the reactants, and the standard transformed Gibbs energy of formation of the
reactants are calculated using isomer group thermodynamics (see Section 4.5- 1 ).
Alberty (1999a) has shown that AfG:' for a biochemical reactant is given by
A,G;O = A,G',' - RTln P (7.7-1)
where AfG;' is the standard transformed Gibbs energy of formation for the species
with the fewest hydrogen atoms and P is the binding polynomial for the reactant.
This equation can be applied to the enzymatic site for fumarase and to the
complexes formed with competitive. inhibitors (Alberty, 2000d).
dNii (PLtotYdpH
-1.75 1
f ..._ _.._ . . _ _ I ...., ,,H
I
I
6 7 8 9
Figure 7.10 Plot of the binding capacity (see equation 7.5-11) for the catalytic site of
fumarase occupied by L-tartrate at 25°C and an ionic strength of 0.01 M. [With permission
from R. A. Alberty, J. Phj~ Chern. B 104, 9929-9934 (2000). Copyright 2000 American
Chemical Society.]