Page 139 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 139
136 Chapter 7 Thermodynamics of the Binding of Ligands by Proteins
-
-- _- _-
-0.25 1
-0.5 !
-0.75
-1 7
-1.25 ;
-1.5 ! - -- ---
--
. --
-1.75 7
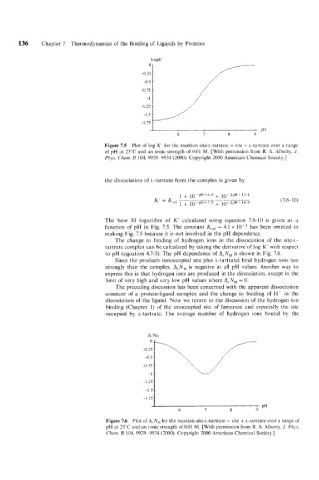
Figure 7.5 Plot of log K' for the reaction site-L-tartrate = site + L-tartrate over a range
of pH at 25°C and an ionic strength of 0.01 M. [With permission from R. A. Alberty, J.
Phys. Chem. B 104, 9929-9934 (2000). Copyright 2000 American Chemical Society.]
the dissociation of L-tartrate from the complex is given by
1 + 10--pH+6.9 + 10-2pH+13.2
(7.6- 10)
K' = 'ref 1 + 10-pH+7.5 + 10-2pH+14.9
The base 10 logarithm of K' calculated using equation 7.6-10 is given as a
function of pH in Fig. 7.5. The constant Kref = 4.1 x lop3 has been omitted in
making Fig. 7.5 because it is not involved in the pH dependence.
The change in binding of hydrogen ions in the dissociation of the site-L-
tartrate complex can be calculated by taking the derivative of log K' with respect
to pH (equation 4.7-5). The pH dependence of ArNH is shown in Fig. 7.6.
Since the products (unoccupied site plus L-tartrate) bind hydrogen ions less
strongly than the complex, A,NH is negative at all pH values. Another way to
express this is that hydrogen ions are produced in the dissociation, except in the
limit of very high and very low pH values where ArNH = 0.
The preceding discussion has been concerned with the apparent dissociation
constant of a protein-ligand complex and the change in binding of H+ in the
dissociation of the ligand. Now we return to the discussion of the hydrogen ion
binding (Chapter 1) of the unoccupied site of fumarase and especially the site
occupied by L-tartrate. The average number of hydrogen ions bound by the
-0.5 i
-0.75 t
-1 1 .=. - . /'
-1.25
-1.5 ;
-1.75 1
#
Figure 7.6 Plot of ArNH for the reaction site-L-tartrate = site + L-tartrate over a range of
pH at 25°C and an ionic strength of 0.01 M. [With permission from R. A. Alberty, J. Phys.
Chem. B 104, 9929 9934 (2000). Copyright 2000 American Chemical Society.]