Page 161 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 161
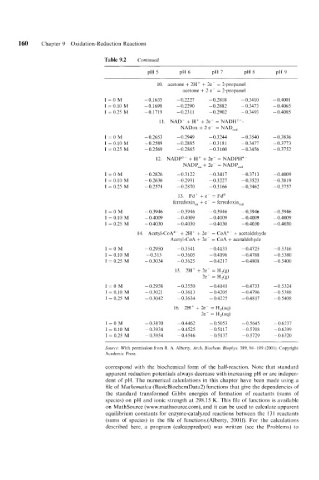
160 Chapter 9 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Table 9.2 Continued
PH 9
10. acetone + 2H' + 2e- = 2-propanol
acetone + 2 e- = 2-propanol
T=OM - 0.1635 - 0.2221 -0.28 I8 -0.3410 - 0.400 1
I = 0.10 M - 0.1698 - 0.2290 -0.2882 - 0.3473 -0.4065
I = 0.25 M -0.1719 -0.2311 - 0.2902 -0.3493 - 0.4085
11. NAD- + H' + 2e- = NADH2--
NADox + 2 e- = NADr,,
I=OM - 0.2653 - 0.2949 -0.3244 -0.3540 -0.3836
I = 0.10 M - 0.2589 -0.2885 -0.3181 -0.3417 -0.3173
I = 0.25 M -0.2569 -0.2865 - 0.3 160 - 0.3456 -0.3152
12. NADP3- + H+ + 2e- = NADPH4
NADPox + 2e- = NADPre,
1=OM - 0.2826 - 0.3122 -0.3411 -0.371 3 - 0.4009
I = 0.10 M - 0.2636 - 0.293 1 - 0.3221 -0.3523 -0.3819
I = 0.25 M - 0.2514 -0.2870 - 0.3166 -0.3462 -0.3757
13. Fd' + e- = Fdo
ferredoxinox + e = ferredoxinred
1=0M - 0.3946 - 0.3946 -0.3946 -0.3946 -0.3946
I = 0.10 M - 0.4009 - 0.4009 - 0.4009 - 0.4009 - 0.4009
I = 0.25 M - 0.4030 - 0.4030 - 0.4030 - 0.4030 - 0.4030
14. Acetyl-CoA4- + 2H' + 2e- = CoA4- + acetaldehyde
Acetyl-CoA + 2e- = CoA + acetaldehyde
I=OM ~ 0.2950 -0.3541 - 0.4133 -0.4125 - 0.53 16
1 = 0.10 M --0.3 13 -0.3605 -0.4196 -0.4788 -0.5380
1 = 0.25 M - 0.3034 -0.3625 -0.421 7 -0.4808 -0.5400
15. 2H' + 2e- = H,(g)
2e- = H2(g)
I=OM - 0.2958 -0.3550 - 0.414 1 -0.4733 -0.5324
I = 0.10 M -0.3021 -0.3613 -0.4205 - 0.4196 -0.5388
I = 0.25 M - 0.3042 - 0.3634 -0.4225 -0.4817 - 0.5408
16. 2H' + 2e- = H,(aq)
2e- = H,(aq)
I=OM - 0.3810 - 0.4462 -0.5053 - 0.5645 - 0.6237
I = 0.10 M ~ 0.3934 -0.4525 -0.5117 -0.5708 - 0.6399
I = 0.25 M ~ 0.3954 - 0.4546 - 0.5137 -0.5129 - 0.6320
Source: With permission from R. A. Alberty. Arch. Biochern. Biopliys. 389, 94- 109 (2001). Copyright
Academic Press.
correspond with the biochemical form of the half-reaction. Note that standard
apparent reduction potentials always decrease with increasing pH or are indepen-
dent of pH. The numerical calculations in this chapter have been made using a
file of Mathematica (BasicBiochemData2) functions that give the dependencies of
the standard transformed Gibbs energies of formation of reactants (sums of
species) on pH and ionic strength at 298.15 K. This file of functions is available
on Mathsource (www.mathsource.com), and it can be used to calculate apparent
equilibrium constants for enzyme-catalyzed reactions between the 13 I reactants
(sums of species) in the file of functions.(Alberty, 2001f). For the calculations
described here, a program (calcappredpot) was written (see the Problems) to