Page 23 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 23
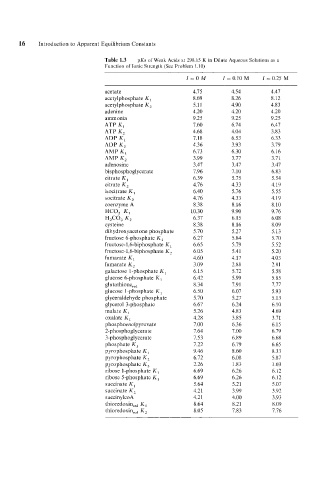
16 Introduction to Apparent Equilibrium Constants
Table 1.3 pKs of Weak Acids at 298.15 K in Dilute Aqueous Solutions as a
Function of Ionic Strength (See Problem 1.10)
Z=OM I = 0.10 M Z = 0.25 M
acetate 4.75 4.54 4.47
acetylphosphate K , 8.69 8.26 8.12
acetylphosphate K, 5.1 1 4.90 4.83
adenine 4.20 4.20 4.20
ammonia 9.25 9.25 9.25
ATP K, 7.60 6.74 6.47
ATP K, 4.68 4.04 3.83
ADP K, 7.18 6.53 6.33
ADP K, 4.36 3.93 3.79
AMP K, 6.73 6.30 6.16
AMP K, 3.99 3.77 3.71
adenosine 3.47 3.47 3.47
bisphosphoglycerate 7.96 7.10 6.83
citrate K, 6.39 5.75 5.54
citrate K, 4.76 4.33 4.19
isocitrate K, 6.40 5.76 5.55
socitrate K, 4.76 4.33 4.19
coenzyme A 8.38 8.16 8.10
HCO, K, 10.30 9.90 9.76
HZCO, K, 6.37 6.15 6.08
cysteine 8.38 8.16 8.09
dihydroxyacetone phosphate 5.70 5.27 5.13
fructose 6-phosphate K , 6.27 5.84 5.70
fructose-l,6-biphosphate K, 6.65 5.79 5.52
fructose-] ,6-biphosphate K, 6.05 5.41 5.20
fumarate K 4.60 4.17 4.03
fumarate K, 3.09 2.88 2.81
galactose l-phosphate K , 6.15 5.72 5.58
glucose 6-phosphate K , 6.42 5.99 5.85
glutathione,,, 8.34 7.91 7.77
glucose 1 -phosphate K , 6.50 6.07 5.93
glyceraldehyde phosphate 5.70 5.27 5.13
glycerol 3-phosphate 6.67 6.24 6.10
malate K, 5.26 4.83 4.69
oxalate K, 4.28 3.85 3.71
phosphoenolpyruvate 7.00 6.36 6.15
2-phosphoglycerate 7.64 7.00 6.79
3-phosphoglycera te 7.53 6.89 6.68
phosphate K, 7.22 6.79 6.65
pyrophosphate K, 9.46 8.60 8.33
pyrophosphate K, 6.72 6.08 5.87
pyrophosphate K, 2.26 1.83 1.69
ribose 1 -phosphate K , 6.69 6.26 6.12
ribose 5-phosphate K,
succinate K , 6.69 6.26 6.12
5.64
5.07
5.21
succinate K, 4.21 3.99 3.92
succinylcoA 4.21 4.00 3.93
thioredoxin,,, K , 8.64 8.21 8.09
thioredoxin,,, K, 8.05 7.83 7.76