Page 287 - Bird R.B. Transport phenomena
P. 287
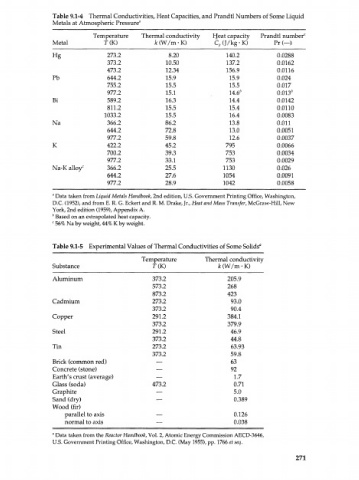
Table 9.1-4 Thermal Conductivities, Heat Capacities, and Prandtl Numbers of Some Liquid
Metals at Atmospheric Pressure"
Temperature Thermal conductivity Heat capacity Prandtl number 0
Metal T(K) к (W/m • K) C (J/kg-K) Pr(—)
p
Hg 273.2 8.20 140.2 0.0288
373.2 10.50 137.2 0.0162
473.2 12.34 156.9 0.0116
Pb 644.2 15.9 15.9 0.024
755.2 15.5 15.5 0.017
977.2 15.1 U.6 b 0.013*
Bi 589.2 16.3 14.4 0.0142
811.2 15.5 15.4 0.0110
1033.2 15.5 16.4 0.0083
Na 366.2 86.2 13.8 0.011
644.2 72.8 13.0 0.0051
977.2 59.8 12.6 0.0037
К 422.2 45.2 795 0.0066
700.2 39.3 753 0.0034
977.2 33.1 753 0.0029
Na-K alloy c 366.2 25.5 ИЗО 0.026
644.2 27.6 1054 0.0091
977.2 28.9 1042 0.0058
" Data taken from Liquid Metals Handbook, 2nd edition, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington,
D.C. (1952), and from E. R. G. Eckert and R. M. Drake, Jr., Heat and Mass Transfer, McGraw-Hill, New
York, 2nd edition (1959), Appendix A.
b
Based on an extrapolated heat capacity.
c
56% Na by weight, 44% К by weight.
Table 9.1-5 Experimental Values of Thermal Conductivities of Some Solids fl
Temperature Thermal conductivity
Substance Г(К) к (W/m • K)
Aluminum 373.2 205.9
573.2 268
873.2 423
Cadmium 273.2 93.0
373.2 90.4
Copper 291.2 384.1
373.2 379.9
Steel 291.2 46.9
373.2 44.8
Tin 273.2 63.93
373.2 59.8
Brick (common red) — 63
Concrete (stone) — 92
Earth's crust (average) — 1.7
Glass (soda) 473.2 0.71
Graphite — 5.0
Sand (dry) — 0.389
Wood (fir)
parallel to axis — 0.126
normal to axis — 0.038
" Data taken from the Reactor Handbook, Vol. 2, Atomic Energy Commission AECD-3646,
U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. (May 1955), pp. 1766 et seq.
271