Page 130 - Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection
P. 130
96 Cha pte r T h ree
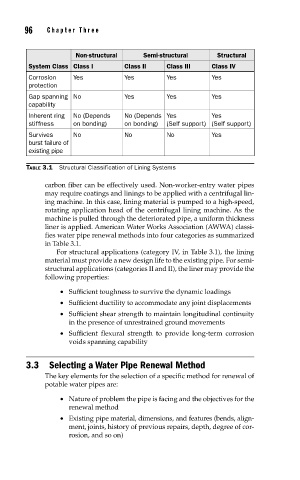
Non-structural Semi-structural Structural
System Class Class I Class II Class III Class IV
Corrosion Yes Yes Yes Yes
protection
Gap spanning No Yes Yes Yes
capability
Inherent ring No (Depends No (Depends Yes Yes
stiffness on bonding) on bonding) (Self support) (Self support)
Survives No No No Yes
burst failure of
existing pipe
TABLE 3.1 Structural Classification of Lining Systems
carbon fiber can be effectively used. Non-worker-entry water pipes
may require coatings and linings to be applied with a centrifugal lin-
ing machine. In this case, lining material is pumped to a high-speed,
rotating application head of the centrifugal lining machine. As the
machine is pulled through the deteriorated pipe, a uniform thickness
liner is applied. American Water Works Association (AWWA) classi-
fies water pipe renewal methods into four categories as summarized
in Table 3.1.
For structural applications (category IV, in Table 3.1), the lining
material must provide a new design life to the existing pipe. For semi-
structural applications (categories II and II), the liner may provide the
following properties:
• Sufficient toughness to survive the dynamic loadings
• Sufficient ductility to accommodate any joint displacements
• Sufficient shear strength to maintain longitudinal continuity
in the presence of unrestrained ground movements
• Sufficient flexural strength to provide long-term corrosion
voids spanning capability
3.3 Selecting a Water Pipe Renewal Method
The key elements for the selection of a specific method for renewal of
potable water pipes are:
• Nature of problem the pipe is facing and the objectives for the
renewal method
• Existing pipe material, dimensions, and features (bends, align-
ment, joints, history of previous repairs, depth, degree of cor-
rosion, and so on)