Page 131 - Tribology in Machine Design
P. 131
Friction, lubrication and wear in lower kinematic pairs 117
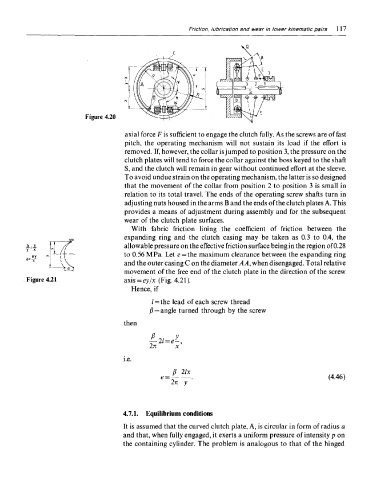
Figure 4.20
axial force F is sufficient to engage the clutch fully. As the screws are of fast
pitch, the operating mechanism will not sustain its load if the effort is
removed. If, however, the collar is jumped to position 3, the pressure on the
clutch plates will tend to force the collar against the boss keyed to the shaft
S, and the clutch will remain in gear without continued effort at the sleeve.
To avoid undue strain on the operating mechanism, the latter is so designed
that the movement of the collar from position 2 to position 3 is small in
relation to its total travel. The ends of the operating screw shafts turn in
adjusting nuts housed in the arms B and the ends of the clutch plates A. This
provides a means of adjustment during assembly and for the subsequent
wear of the clutch plate surfaces.
With fabric friction lining the coefficient of friction between the
expanding ring and the clutch casing may be taken as 0.3 to 0.4, the
allowable pressure on the effective friction surface being in the region of 0.28
to 0.56 MPa. Let e — the maximum clearance between the expanding ring
and the outer casing C on the diameter A A, when disengaged. Total relative
movement of the free end of the clutch plate in the direction of the screw
Figure 4.21 axis = ey/x (Fig. 4.21).
Hence, if
/ = the lead of each screw thread
/? = angle turned through by the screw
then
4.7.1. Equilibrium conditions
It is assumed that the curved clutch plate, A, is circular in form of radius a
and that, when fully engaged, it exerts a uniform pressure of intensity p on
the containing cylinder. The problem is analogous to that of the hinged