Page 358 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 358
31 8 Norman P. Barnes
nonlinear crystal. As the average power increases, the generated heat and the
concomitant thermal gradients increase. Consequently, the effective volume of
the nonlinear crystal decreases, which, in turn, eventually limits the average
power that can be produced.
Average power limitations will depend on the geometry of the nonlinear
crystal and the interacting beams. When considering the geometry of the nonlin-
ear crystal, actual cooling conditions in many instances can be approximated by
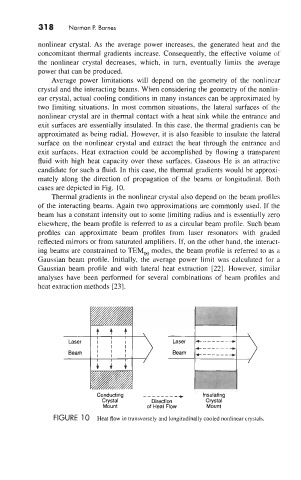
two limiting situations. In most common situations, the lateral surfaces of the
nonlinear crystal are in thermal contact with a heat sink while the entrance and
exit surfaces are essentially insulated. In this case, the thermal gradients can be
approximated as being radial. However, it is also feasible to insulate the lateral
surface on the nonlinear crystal and extract the heat through the entrance and
exit surfaces. Heat extraction could be accomplished by flowing a transparent
fluid with high heat capacity over these surfaces. Gaseous He is an attractive
candidate for such a fluid. In this case, the thermal gradients would be approxi-
mately along the direction of propagation of the beams or longitudinal. Both
cases are depicted in Fig. 10.
Thermal gradients in the nonlinear crystal also depend on the beam profiles
of the interacting beams. Again two approximations are commonly used. If the
beam has a constant intensity out to some limiting radius and is essentially zero
elsewhere, the beam profile is referred to as a circular beam profile. Such beam
profiles can approximate beam profiles from laser resonators with graded
reflected mirrors or from saturated amplifiers. If, on the other hand, the interact-
ing beams are constrained to TEM, modes, the beam profile is referred to as a
Gaussian beam profile. Initially, the average power limit was calculated for a
Gaussian beam profile and with lateral heat extraction [22]. However, similar
analyses have been performed for several combinations of beam profiles and
heat extraction methods [23].
Conducting - - - - - - - - + Insulating
Crystal Direction Crystal
Mount of Heat Flow Mount
FIGURE 1 0 Heat flow in transversely and longitudinally cooled nonlinear crystals.