Page 363 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 363
7 Optical Parametric Osciliators 323
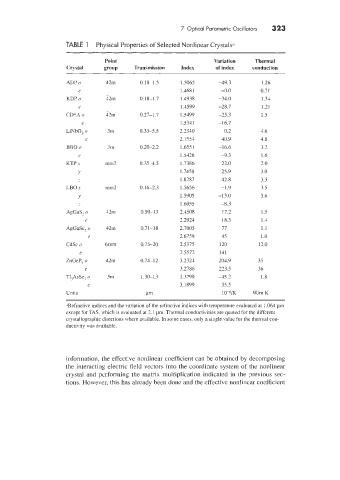
TABLE 1 Physical Properties of Selected Nonlinear Crystalsa
Point Variation Thermal
Crystal group Transmission Index of index conduction
ADP 0 42m 0.18-1.5 1.5065 49.3 1.26
e 1.468 1 =o.o 0.71
-
KDP o 32m 0.18-1.7 14938 -34.0 1.3;
e 1.4599 -28.7 1.21
CD*A 0 Z2m 0.27-1.7 1.5499 -23.3 1.5
e 1.5311 -16.7
LiNbO, o 3m 0.33-5.5 2.2340 0.2 1.6
e 2.1553 40.9 1.8
BBO o 3m 0.20-2.2 1.655 1 -16.6 12
e 1.5126 -9.3 1.6
KTP .I- mm2 0.351.5 1.7386 22.0 2.0
Y 1.7458 25.9 30
1.8287 12.8 3.3
LBO .Y mm2 0.16-2.3 1.5656 -1.9 35
v 1.5905 -13.0 3.6
1.6055 -8,3
AgGaS, o 32m 0.50-13 2.1508 17.2 1.5
e 2.2921 18.3 13
.4gGaSe, o 42m 0.71-18 2.7005 17 1.1
2 6759 45 1 .o
CdSe o 6mm 0.75-20 2.5375 120 12.0
e 2.5572 141
ZnGeP, o 42m 0.71-12 3.2324 204.9 35
e 3.2786 223.5 36
Tl,AsSe, o 3m 1.30-13 3.3799 -45 2 1.8
..
e 3.1899 35.5
Units Pm 10-6/K W/m K
.Refractive indices and the lariation of the refractive indices with temperature evaluated at 1.064 pin
esczpt for T?&, which is evaluated at 2.1 pm. Thermal conductivities are quoted for the different
crytallopaphic directions where available. In some cases, only a single value for the thermal con-
ductivity was available.
information, the effective nonlinear coefficient can be obtained by decomposing
the interacting electric field vectors into the coordinate system of the nonlinear
crystal and performing the matrix multiplication indicated in the previous sec-
tions. However, this has already been done and the effective nonlinear coefficient