Page 401 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 401
8 Tunable External-Cavity Semiconductor Lasers 36 1
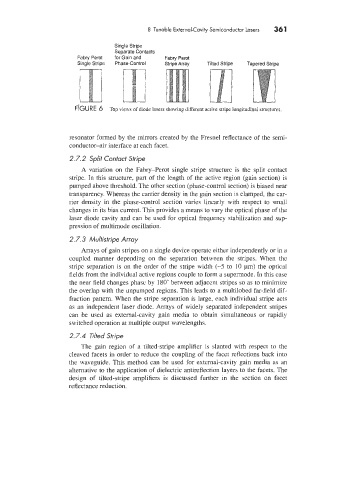
Single Stripe
Separate Contacts
Fabry Perot for Gain and Fabry Perot
Single Stripe Phase-Control Stripe Array Tilted Stripe Tapered Stripe
flGURE 6 Top viem of diode lasers showing different active smpe longitudinal structures
resonator formed by the mirrors created by the Fresnel reflectance of the semi-
conductor-air interface at each facet.
2.7.2 Split Contact Stripe
A variation on the Fabry-Perot single stripe strucmre is the split contact
stripe. In this structure. part of the length of the active region (gain section) is
pumped above threshold. The other section (phase-control section) is biased near
transparency. Whereas the carrier density in the gain section is clamped. the car-
rier density in the phase-control section varies linearly with respect to small
changes in its bias current. This provides a means to vary the optical phase of the
laser diode cavity and can be used for optical frequency stabilization and sup-
pression of multimode oscillation.
2.7.3 Muhistripe Array
Arrays of gain stripes on a single device operate either independently or in a
coupled manner depending on the separation between the stripes. When the
stripe separation is on the order of the stripe width (-5 to 10 pm) the optical
fields from the individual active regions couple to form a superrnode. In this case
the near field changes phase by 180" between adjacent stripes so as to minimize
the overlap with the unpumped regions. This leads to a multilobed far-field dif-
fraction pattern. When the stripe separation is large, each individual stripe acts
as an independent laser diode. Arrays of widely separated independent stripes
can be used as external-cavity gain media to obtain simultaneous or rapidly
switched operation at multiple output wavelengths.
2.7.4 Tilted Stripe
The gain region 3f a tilted-stripe amplifier is slanted with respect to the
cleaved facets in order to reduce the coupling of the facet reflections back into
the waveguide. This method can be used for external-cavity gain media as an
alternative to the application of dielectric antireflection layers to the facets. The
design of tilted-stripe amplifiers is discussed further in the section on facet
reflectance reduction.