Page 469 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 469
8 Tunable External-Cavity Semiconductor Lasers 29
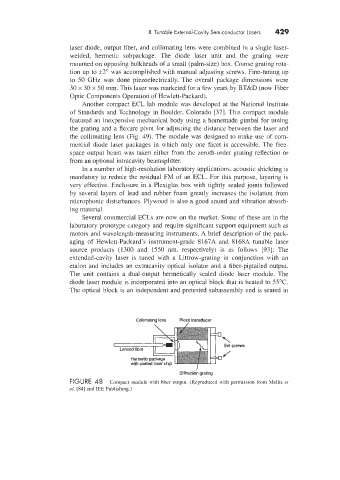
laser diode, output fiber, and collimating lens were combined in a single laser-
welded, hermetic subpackage. The diode laser unit and the grating were
mounted on opposing bulkheads of a small (palm-size) box. Coarse grating rota-
tion up to rfr2" was accomplished with manual adjusting screws. Fine-tuning up
to 50 GHz was done piezoelectrically. The overall package dimensions were
30 x 30 x 50 mm. This laser was marketed for a few years by BT&D (now Fiber
Optic Components Operation of Hen lett-Packard).
Another compact ECL lab module was developed at the National Institute
of Standards and Technology in Boulder. Colorado [37]. This compact module
featured an inexpensive mechanical body using a homemade gimbal for tuning
the grating and a flexure pivot for adjusting the distance between the laser and
the collimating lens (Fig. 39). The module was designed to make use of com-
mercial diode laser packages in which only one facet is accessible. The fre2-
space output beam was taken either from the zeroth-order grating reflection or
from an optional intracavity beamsplitter.
In a number of high-resolution laboratory applications. acoustic shielding is
mandatory to reduce the residual FM of an ECL. For this purpose, layering is
very effective. Enclosure in a Plexiglas box with tightly sealed joints followed
by sekeral layers of lead and rubber foam greatly increases the isolation from
microphonic disturbances. Plywood is also a good sound and vibration absorb-
ing material.
Several commercial ECLs are nom' on the market. Some of these are in the
laboratory prototype category and require significant support equipment such as
motors and wavelength-measuring instruments. ,4 brief description of the pack-
aging of Hewlett-Packard's instrument-grade 8 167A and 8 168k tunable laser
source products (1300 and 1550 nm. respectively) is as follows [93]: The
extended-cavity laser is tuned with a Littrow-grating in conjunction with an
etalon and includes an extracavity optical isolator and a fiber-pigtailed output.
The unit contains a dual-output hermetically sealed diode laser module. The
diode laser module is incorporated into an optical block that is heated to 55°C.
The optical block is an independent and pretested subassembly and is seated in
Collimating lens Piezo transducer
z
Set screws
J
Diffraction grating
FIGURE 48 Compact module with fiber output. (Reproduced with permission from hlellis et
a/. [84] and IEE Publishing.)