Page 178 - Understanding Automotive Electronics
P. 178
2735 | CH 5 Page 165 Tuesday, March 10, 1998 11:10 AM
THE BASICS OF ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROL 5
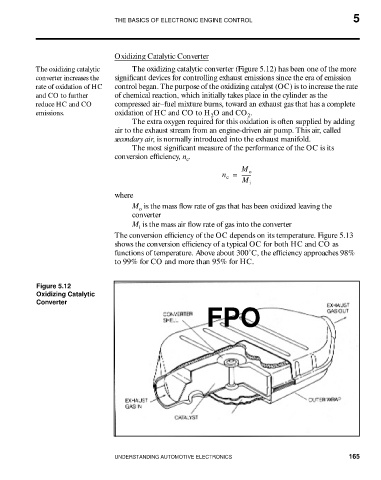
Oxidizing Catalytic Converter
The oxidizing catalytic The oxidizing catalytic converter (Figure 5.12) has been one of the more
converter increases the significant devices for controlling exhaust emissions since the era of emission
rate of oxidation of HC control began. The purpose of the oxidizing catalyst (OC) is to increase the rate
and CO to further of chemical reaction, which initially takes place in the cylinder as the
reduce HC and CO compressed air–fuel mixture burns, toward an exhaust gas that has a complete
emissions. oxidation of HC and CO to H O and CO .
2
2
The extra oxygen required for this oxidation is often supplied by adding
air to the exhaust stream from an engine-driven air pump. This air, called
secondary air, is normally introduced into the exhaust manifold.
The most significant measure of the performance of the OC is its
conversion efficiency, n .
c
M
n = ------- o
c
M i
where
M is the mass flow rate of gas that has been oxidized leaving the
o
converter
M is the mass air flow rate of gas into the converter
i
The conversion efficiency of the OC depends on its temperature. Figure 5.13
shows the conversion efficiency of a typical OC for both HC and CO as
functions of temperature. Above about 300˚C, the efficiency approaches 98%
to 99% for CO and more than 95% for HC.
Figure 5.12
Oxidizing Catalytic
Converter
FPO
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS 165