Page 410 - Understanding Automotive Electronics
P. 410
2735 | CH 11 Page 397 Tuesday, March 10, 1998 1:30 PM
FUTURE AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS 11
the next signpost is reached, the need for signposts at every intersection, and
the requirement for a large number of codes. Thus, in spite of the high accuracy
of this system, it inherently requires a huge investment in infrastructure.
Dead Reckoning Navigation
Dead reckoning navigation is a method of determining present position
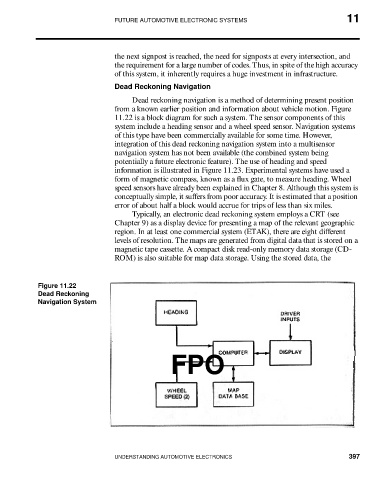
from a known earlier position and information about vehicle motion. Figure
11.22 is a block diagram for such a system. The sensor components of this
system include a heading sensor and a wheel speed sensor. Navigation systems
of this type have been commercially available for some time. However,
integration of this dead reckoning navigation system into a multisensor
navigation system has not been available (the combined system being
potentially a future electronic feature). The use of heading and speed
information is illustrated in Figure 11.23. Experimental systems have used a
form of magnetic compass, known as a flux gate, to measure heading. Wheel
speed sensors have already been explained in Chapter 8. Although this system is
conceptually simple, it suffers from poor accuracy. It is estimated that a position
error of about half a block would accrue for trips of less than six miles.
Typically, an electronic dead reckoning system employs a CRT (see
Chapter 9) as a display device for presenting a map of the relevant geographic
region. In at least one commercial system (ETAK), there are eight different
levels of resolution. The maps are generated from digital data that is stored on a
magnetic tape cassette. A compact disk read-only memory data storage (CD-
ROM) is also suitable for map data storage. Using the stored data, the
Figure 11.22
Dead Reckoning
Navigation System
FPO
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS 397