Page 94 - Understanding Automotive Electronics
P. 94
2735 | CH 3 Page 81 Tuesday, March 10, 1998 11:03 AM
ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTALS 3
out. The system’s output (the light from the bulb) is either on or off. The on
state means the door is open; the off state means it is shut.
Digital circuits also can In electronic digital systems, a transistor is used as a switch. Remember
use transistors. In a digi- that the transistor has three operating regions: cutoff, active, and saturation. If
tal circuit, a transistor is only the saturation or cutoff regions are used, the transistor acts like a switch.
in either one of two When in saturation, the transistor is on and has very low resistance; when in
modes of operation: on, cutoff, it is off and has very high resistance. In digital circuits, the control input
conducting at satura- to the transistor switch must be capable of either saturating the transistor or
tion; or off, in the cutoff turning it off without allowing operation in the active region. In Figure 3.2c,
state. the on condition is indicated by a very low collector-to-emitter voltage and the
off condition by a collector-to-emitter voltage equal to the supply voltage.
Binary Number System
Combinations of digital Digital circuits function by representing various quantities numerically
circuits are capable of using a binary number system. In a binary number system, all numbers are
representing numbers in represented using only the symbols 1 (one) and 0 (zero) arranged in the form of
a binary number system. a place position number system. Electronically, these symbols can be
represented by transistors in either saturation or cutoff. Before proceeding with
a discussion of digital circuits, it is instructive to review the binary number
system briefly.
The binary number system uses only two digits, 0 or 1, and is called a
base 2 system. The decimal system uses 10 digits, 0 through 9, and is called a
base 10 system. In the decimal system, numbers are grouped from right to left
0
with the first digit representing the ones’ place (10 ), the second digit the tens’
2
1
place (10 ), the third digit the hundreds’ place (10 ), and so on. Each place
increases in value by a power of 10.
In the binary system, numbers are also grouped from right to left. The
0
rightmost digit is in the ones’ place (2 ) and, because only the numbers 0 and 1
1
can be represented, the second digit must be the twos’ place (2 ), the third digit
2
3
the fours’ place (2 ), the fourth digit the eights’ place (2 ), and so on. Each
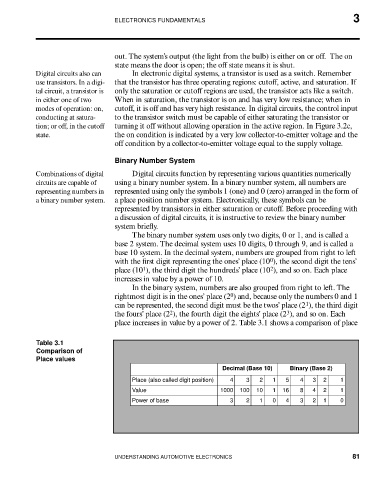
place increases in value by a power of 2. Table 3.1 shows a comparison of place
Table 3.1
Comparison of
Place values
Decimal (Base 10) Binary (Base 2)
Place (also called digit position) 4 3 2 1 5 4 3 2 1
Value 1000 100 10 1 16 8 4 2 1
Power of base 3 2 1 0 4 3 2 1 0
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS 81