Page 204 - Uninterruptible Power Supplies
P. 204
Batteries
202 Chapter Seven
Electrochemical efficiency related to battery state of charge
Electrochemical
efficiency
State of charge Reactions (% of current)
Maintenance in (i) Discharge (self) 100% equivalent
fully charged current
condition (ii) Float recharge 10%
(compensation)
(iii) Electrolysis 90%
Approximately 80% (i) Discharge 100%
state of charge (ii) Recharge 100% at 80% SOC* —
10% at 100% SOC*
(iii) Electrolysis NIL at 80% SOC* —
90% at 100% SOC*
Fully discharged (i) Discharge 100%
to approximately
80% state of (ii) Recharge 100%
charge
*SOC = ‘state of charge’
Figure 7.19 Electrochemical efficiency related to battery state of charge.
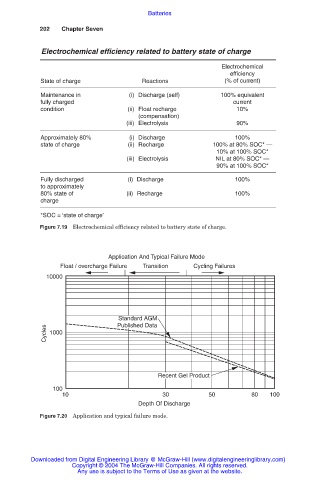
Application And Typical Failure Mode
Float / overcharge Failure Transition Cycling Failures
10000
Standard AGM
Published Data
Cycles 1000
Recent Gel Product
100
10 30 50 80 100
Depth Of Discharge
Figure 7.20 Application and typical failure mode.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.