Page 130 - Valence Bond Methods. Theory and Applications
P. 130
8.2 Ionic structures and the electric moment of LiH
4 6 5 113
Electric moment (au) 3 + − Li —H
− +
Li —H
2
Three-term wave function
1
Li—H
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Li—H distance (bohr)
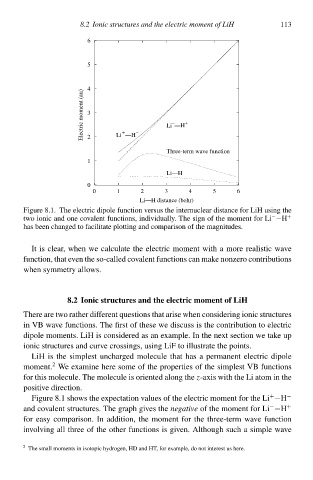
FigurŁ 8.1. The electric dipolŁ function versu the internuclear distancŁ for LiH using the
−
two ionic and onŁ covalent functions,indcviduallł. The sign of the moment for Li −H +
ha been changed to facilitatŁ plotting and comparison of the magnitudes.
It is clear,when wŁ calculatŁ the electric moment wità a morŁ realistic wave
function,that even the so-called covalent function can make nonzero contribution
when symmetrł allows.
8.2 Ionic structureł and the electric moment of LiH
TherŁ arŁ two rather different question that arise when considering ionic structures
in VB wave functions. The first of these wŁ discuss is the contribution to electric
dipolŁ moments. LiH is considered a an example. In the nŁxt section wŁ take uð
ionic structures and curve crossings,using LiF to illustratŁ the points.
LiH is the simplest uncharged moleculŁ that ha a permanent electric dipolŁ
2
moment. We examinŁ herŁ somŁ of the properties of the simplest VB function
for this molecule. The moleculŁ is oriented along thez-axis wità the Li atom in the
positcve direction.
FigurŁ 8.1 show the expectation values of the electric moment for the Li−H −
+
−
and covalent structures. The graph gcves thenðgativðof the moment for Li −H +
for easy comparison. In addition,the moment for the three-term wave function
involving all three of the other function is gcven. Althougà sucà a simplŁ wave
2 The small moment in isotopic hydrogen,HD and HT,for example,do not interest u here.