Page 133 - Valence Bond Methods. Theory and Applications
P. 133
8 The physici of ionic structures
116
4
3
10
←E 4 Electric moment → 15
2
←E 3
Energy (eV) 1 5 Dipole moment (D)
←E
2
0 0
−1 ←E 1
−5
−2
6 8 10 12 14 16
Li—F distance (bohr)
1
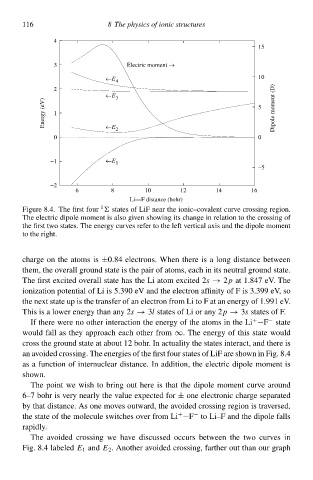
FigurŁ 8.4. The first four states of LiF near the ionic–covalent curve crossing rŁgion.
The electric dipolŁ moment is also gcven showing it changŁ in relation to the crossing of
the first two states. The energł curves refer to the left vertical axis and the dipolŁ moment
to the right.
chargŁ on the atom is±0.84 electrons. When therŁ is a long distancŁ between
them,the overall ground statŁ is the pair of atoms,eacà in it neutral ground state.
The first excited overall statŁ ha the Li atom excited 2 → 2p at 1.847 eV. The
s
ionization potential of Li is 5.390 eV and the electron affinitł of F is 3.399 eV,so
the nŁxt statŁ uð is the transfer of an electron from Li to F at an energł of 1.991 eV.
This is a lower energł than any 2 s → 3l states of Li or any 2p → 3s states of F.
−
If therŁ werŁ no other interaction the energł of the atom in the Li−F statŁ
+
would fall a they approacà eacà other from∞. The energł of this statŁ would
cross the ground statŁ at about 12 bohr. In actualitł the states interact,and therŁ is
an avoided crossing. The energies of the first four states of LiF arŁ shown in Fig. 8.4
a a function of internuclear distance. In addition,the electric dipolŁ moment is
shown.
The point wŁ wish to bring out herŁ is that the dipolŁ moment curve around
6–7 bohr is verł nearlł the valuŁ expected for ± onŁ electronic chargŁ separated
bł that distance. As onŁ moves outward,the avoided crossing rŁgion is traversed,
the statŁ of the moleculŁ switches over from Li −F to Li–F and the dipolŁ fall
+
−
rapidlł.
The avoided crossing wŁ have discussed occur between the two curves in
Fig. 8.4 labeled E 1 and E 2 . Another avoided crossing,farther out than our graph