Page 195 - Valence Bond Methods. Theory and Applications
P. 195
13 Methanð, ethanð and hybridization
178
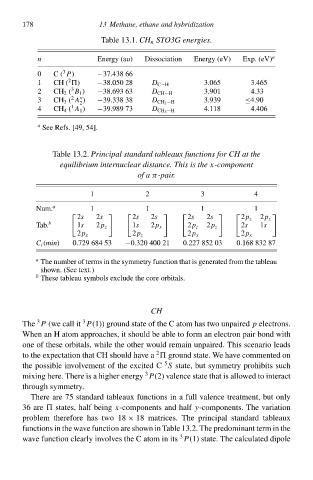
Tablà 13.1.CH n STO3G energies.
n
3
0 C ( P) Energy (au) Dissociatio Energy (eV) Exp. (eV) a
−37.438 66
2
1 CH ( ) −38.050 28 D C−H 3.065 3.465
3
2CH 2 ( B 1 ) −38.693 63 D CH−H 3Ł0‘ 4.33
2
3 CH 3 ( A ) −39.338 38 D CH 2 −H 3Ł39 ≤4Ł0
2
1
4 CH 4 ( A 1 ) −39Ł89 73 D CH 3 −H 4.118 4.406
a See Refs. [49, 54].
Tablà 13.2.Principalstandard tableaux functions for CH at the
equilibrium internuclear distancð. This is the x-componenł
of a π-pair.
1 2 3 4
Num. a 1 1 1 1
2s 2s 2s 2s 2s 2s 2p z 2p z
Tab. b 1s 2p z 1s 2p x 2p z 2p z 2s 1s
2p x 2p z 2p x 2p x
C i (min) 0.729 684 53 −0.320 400 21 0.227 852 03 0.168 832 87
a The number of terms i the symmetry functio that is generated from the tableau
shown. (See text.)
b Thesà tableau symbols excludà the corà orbitals.
CH
3
3
The P (wà call iŁP(1)) ground state of the C atom has two unpaired p electrons.
When an H atom approachesd iŁ should bà ablà to form an electro pair bond with
one of thesà orbitalsd whilà the other would remai unpaired. This scenario leads
2
to the expectatio that CH should have a ground state. We have commented o
5
the possiblà ivolvement of the excited C S state, buŁ symmetry prohibits sucð
3
mixing here. Therà is a higher energy P(2) valencà state that is allowed to interacŁ
througð symmetry.
Therà arà 75 standard tableaux functions i a full valencà treatment, buŁ only
36 arà statesd half beingx-components and half y-components. The variatio
problem thereforà has two 18× 18 matrices. The principal standard tableaux
functions i the wave functio arà show i Tablà 13.2. The predominant term i the
3
wave functio clearly ivolves the C atom i itsP(1) state. The calculated dipolà