Page 124 - Vibrational Spectroscopic Imaging for Biomedical Applications
P. 124
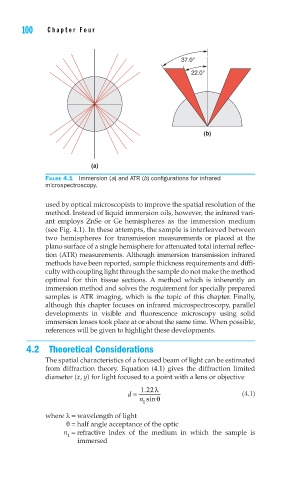
100 Cha pte r F o u r
37.0°
22.0°
(b)
(a)
FIGURE 4.1 Immersion (a) and ATR (b) confi gurations for infrared
microspectroscopy.
used by optical microscopists to improve the spatial resolution of the
method. Instead of liquid immersion oils, however, the infrared vari-
ant employs ZnSe or Ge hemispheres as the immersion medium
(see Fig. 4.1). In these attempts, the sample is interleaved between
two hemispheres for transmission measurements or placed at the
plano surface of a single hemisphere for attenuated total internal reflec-
tion (ATR) measurements. Although immersion transmission infrared
methods have been reported, sample thickness requirements and diffi-
culty with coupling light through the sample do not make the method
optimal for thin tissue sections. A method which is inherently an
immersion method and solves the requirement for specially prepared
samples is ATR imaging, which is the topic of this chapter. Finally,
although this chapter focuses on infrared microspectroscopy, parallel
developments in visible and fluorescence microscopy using solid
immersion lenses took place at or about the same time. When possible,
references will be given to highlight these developments.
4.2 Theoretical Considerations
The spatial characteristics of a focused beam of light can be estimated
from diffraction theory. Equation (4.1) gives the diffraction limited
diameter (x, y) for light focused to a point with a lens or objective
122 λ
.
d = (4.1)
n sinθ
1
where λ= wavelength of light
θ= half angle acceptance of the optic
n = refractive index of the medium in which the sample is
1
immersed