Page 297 - Vibrational Spectroscopic Imaging for Biomedical Applications
P. 297
272 Cha pte r Ni ne
influence of heat generated noise (dark current). To reduce the noise
generated in reading out the camera, slow readout speeds are used.
A next generation of CCD detectors that can be useful in Raman
imaging is now emerging: the electron multiplied CCD (EMCCD). It
has been available for some time for UV and VIS excitation, but now
EMCCDs that have a better sensitivity in the NIR have become
available. This type of detector is especially useful for high-speed,
low-signal applications that are limited by the readout noise of the
CCD. By amplification of the signal, the readout noise that increases
with higher readout speed becomes much smaller compared to the
signal noise (shot noise). However, the amplification process itself
also generates noise and there is an additional (spurious) noise
induced when shifting the charge toward the readout register, so for
applications that are limited by signal noise this is not an improve-
ment, although they may benefit from enabling a higher read out
speed.
9.3 Imaging Techniques
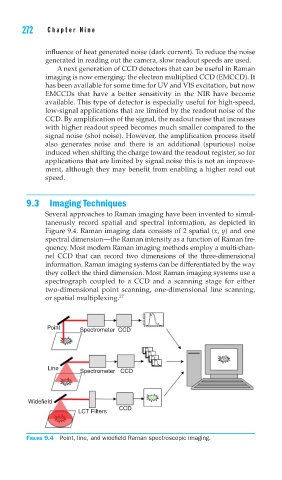
Several approaches to Raman imaging have been invented to simul-
taneously record spatial and spectral information, as depicted in
Figure 9.4. Raman imaging data consists of 2 spatial (x, y) and one
spectral dimension—the Raman intensity as a function of Raman fre-
quency. Most modern Raman imaging methods employ a multi-chan-
nel CCD that can record two dimensions of the three-dimensional
information. Raman imaging systems can be differentiated by the way
they collect the third dimension. Most Raman imaging systems use a
spectrograph coupled to a CCD and a scanning stage for either
two-dimensional point scanning, one-dimensional line scanning,
or spatial multiplexing. 27
Point Spectrometer CCD
Line
Spectrometer CCD
Widefield
CCD
LCT Filters
FIGURE 9.4 Point, line, and widefi eld Raman spectroscopic imaging.