Page 91 - Vibrational Spectroscopic Imaging for Biomedical Applications
P. 91
Sample Pr eparation of Cells and T issue 67
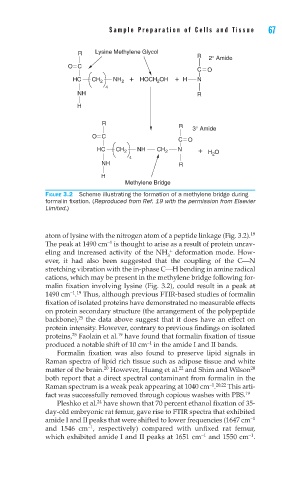
R Lysine Methylene Glycol
R 2° Amide
O C
C O
HC CH 2 NH 2 + HOCH OH + H N
2
4
NH R
H
R
R
3° Amide
O C
C O
HC CH 2 NH CH 2 N + H O
2
4
NH R
H
Methylene Bridge
FIGURE 3.2 Scheme illustrating the formation of a methylene bridge during
formalin fi xation. (Reproduced from Ref. 19 with the permission from Elsevier
Limited.)
atom of lysine with the nitrogen atom of a peptide linkage (Fig. 3.2). 19
−1
The peak at 1490 cm is thought to arise as a result of protein unrav-
+
eling and increased activity of the NH deformation mode. How-
3
ever, it had also been suggested that the coupling of the C⎯N
stretching vibration with the in-phase C⎯H bending in amine radical
cations, which may be present in the methylene bridge following for-
malin fixation involving lysine (Fig. 3.2), could result in a peak at
−1 19
1490 cm . Thus, although previous FTIR-based studies of formalin
fixation of isolated proteins have demonstrated no measurable effects
on protein secondary structure (the arrangement of the polypeptide
backbone), the data above suggest that it does have an effect on
25
protein intensity. However, contrary to previous findings on isolated
proteins, Faolain et al. have found that formalin fixation of tissue
25
19
−1
produced a notable shift of 10 cm in the amide I and II bands.
Formalin fixation was also found to preserve lipid signals in
Raman spectra of lipid rich tissue such as adipose tissue and white
22
20
matter of the brain. However, Huang et al. and Shim and Wilson 20
both report that a direct spectral contaminant from formalin in the
−1 20,22
Raman spectrum is a weak peak appearing at 1040 cm . This arti-
fact was successfully removed through copious washes with PBS. 19
Pleshko et al. have shown that 70 percent ethanol fixation of 35-
24
day-old embryonic rat femur, gave rise to FTIR spectra that exhibited
amide I and II peaks that were shifted to lower frequencies (1647 cm −1
−1
and 1546 cm , respectively) compared with unfixed rat femur,
−1
which exhibited amide I and II peaks at 1651 cm and 1550 cm .
−1