Page 274 - Vogel's TEXTBOOK OF QUANTITATIVE CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
P. 274
9 CAS CHROMATOCRAPHV
Time or volume of carrier gas
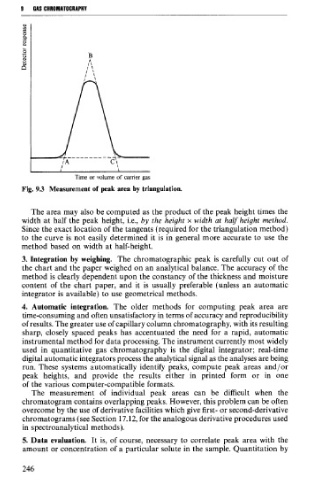
Fig. 93 Measurement of peak area by triangulation.
The area may also be computed as the product of the peak height times the
width at half the peak height, i.e., by ~he height x width ut half height method.
Since the exact location of the tangents (required for the triangulation method)
to the curve is not easily determined it is in general more accurate to use the
method based on width at half-height.
3. Integration by weighing. The chromatographic peak is carefully cut out of
the chart and the paper weighed on an analytical balance. The accuracy of the
method is clearly dependent upon the constancy of the thickness and moisture
content of the chart paper, and it is usually preferable (unless an automatic
integrator is available) to use geometrical methods.
4. Automatic integration. The older methods for computing peak area are
time-consuming and often unsatisfactory in terms of accuracy and reproducibility
of results. The greater use of capillary column chromatography, with its resulting
sharp, closely spaced peaks has accentuated the need for a rapid, automatic
instrumental method for data processing. The instrument currently most widely
used in quantitative gas chromatography is the digital integrator; real-time
digital automatic integrators process the analytical signal as the analyses are being
run. These systems automatically identify peaks, compute peak areas and/or
peak heights, and provide the results either in printed form or in one
of the various computer-compatible formats.
The measurement of individual peak areas can be difficult when the
chromatogram contains overlapping peaks. However, this problem can be often
overcome by the use of derivative facilities which give first- or second-derivative
chromatograms (see Section 17.12, for the analogous derivative procedures used
in spectroanalytical methods).
5. Data evaluation. It is, of course, necessary to correlate peak area with the
amount or concentration of a particular solute in the sample. Quantitation by