Page 524 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 524
CAT3525_C15.qxd 1/27/2005 12:40 PM Page 495
Incineration of Hazardous Wastes 495
combustion chamber. The heat from the combustion gas flowing on the outside of the firebox is
transferred to the water within the boiler or waterwall tubes.
Wastes designated as hazardous may be combusted in industrial boilers provided that the wastes
are hazardous solely based on the characteristic of ignitability. Wastes combusted in this manner
usually occur as liquids that are generated on-site. Examples include aliphatic and aromatic sol-
vents, alcohols, and other highly volatile hydrocarbons. The U.S. EPA has required field tests of
operating facilities in destroying hazardous wastes in standard boilers. The tested boilers achieved
performance ratings close to 99.99% DRE.
During day-to-day operations the interior of a boiler becomes dirty due to the accumulation of
particulate matter on the surface of the boiler or waterwall tubes. Such coatings result in reduced
heat transfer. To address the accumulation of particles, a boiler periodically blows high-velocity air
or steam into the unit to scour surfaces. This process is known as soot blowing and is an important
consideration when designing a trial burn. During soot blowing, a combination of previously
deposited metals, soot, and particulate matter is released. This pulse of particulates enters the air
pollution control system. Because of such particulate surges, part of the trial burn must be con-
ducted under soot blowing conditions (U.S. EPA, 1992).
The advantage of the disposal of hazardous wastes in a boiler is a reduction in cost to the waste
generator compared with on- or off-site incineration. The facility obtains a fuel value from the waste,
and cost savings are accrued from not having to dispose of the waste in an RCRA regulated process.
Also, the waste does not have to be transported to a disposal facility. One disadvantage of hazardous
waste incineration in boilers is that the process is not closely regulated and may be subject to acci-
dents or misuse.
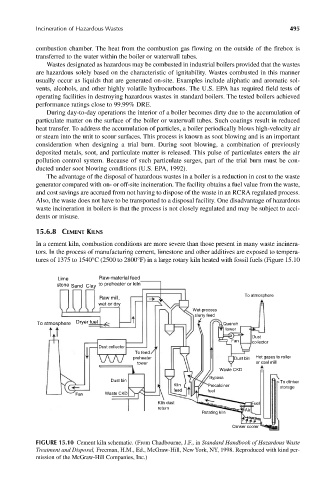
15.6.8 CEMENT KILNS
In a cement kiln, combustion conditions are more severe than those present in many waste incinera-
tors. In the process of manufacturing cement, limestone and other additives are exposed to tempera-
tures of 1375 to 1540°C (2500 to 2800°F) in a large rotary kiln heated with fossil fuels (Figure 15.10
Lime Raw-material feed
to preheater or kiln
stone Sand Clay
To atmosphere
Raw mill,
wet or dry
Wet-process
slurry feed
To atmosphere Dryer fuel Quench
tower
Dust
Fan collector
Dust collector
To feed
preheater Dust bin Hot gases to roller
tower or coal mill
Waste CKD
Bypass
Dust bin To clinker
Kiln Precalciner storage
feed fuel
Fan Waste CKD
Kiln dust Fuel
return Air
Rotating kiln
Clinker cooler
FIGURE 15.10 Cement kiln schematic. (From Chadbourne, J.F., in Standard Handbook of Hazardous Waste
Treatment and Disposal, Freeman, H.M., Ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1998. Reproduced with kind per-
mission of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.)