Page 217 - Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
P. 217
Ash Handling and Recycling 183
operates continuously and uses a blower to drive an eductor that pulls ash from
the collection chamber and mixes it with transport air. The dilute-phase con-
veyance system is designed to transport ash at high velocity and low density.
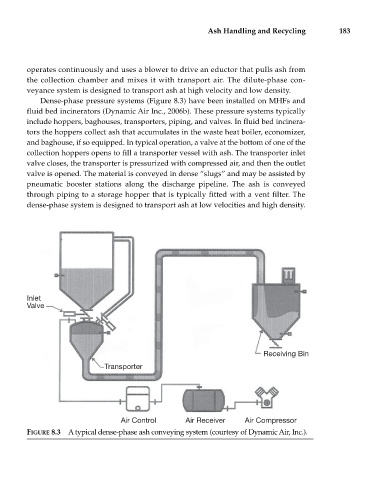
Dense-phase pressure systems (Figure 8.3) have been installed on MHFs and
fluid bed incinerators (Dynamic Air Inc., 2006b). These pressure systems typically
include hoppers, baghouses, transporters, piping, and valves. In fluid bed incinera-
tors the hoppers collect ash that accumulates in the waste heat boiler, economizer,
and baghouse, if so equipped. In typical operation, a valve at the bottom of one of the
collection hoppers opens to fill a transporter vessel with ash. The transporter inlet
valve closes, the transporter is pressurized with compressed air, and then the outlet
valve is opened. The material is conveyed in dense “slugs” and may be assisted by
pneumatic booster stations along the discharge pipeline. The ash is conveyed
through piping to a storage hopper that is typically fitted with a vent filter. The
dense-phase system is designed to transport ash at low velocities and high density.
Inlet
Valve
Receiving Bin
Transporter
Air Control Air Receiver Air Compressor
FIGURE 8.3 A typical dense-phase ash conveying system (courtesy of Dynamic Air, Inc.).