Page 319 - Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
P. 319
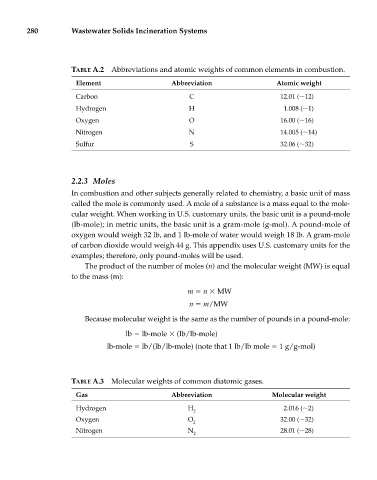
280 Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
TABLE A.2 Abbreviations and atomic weights of common elements in combustion.
Element Abbreviation Atomic weight
Carbon C 12.01 ( 12)
Hydrogen H 1.008 ( 1)
Oxygen O 16.00 ( 16)
Nitrogen N 14.005 ( 14)
Sulfur S 32.06 ( 32)
2.2.3 Moles
In combustion and other subjects generally related to chemistry, a basic unit of mass
called the mole is commonly used. A mole of a substance is a mass equal to the mole-
cular weight. When working in U.S. customary units, the basic unit is a pound-mole
(lb-mole); in metric units, the basic unit is a gram-mole (g-mol). A pound-mole of
oxygen would weigh 32 lb, and 1 lb-mole of water would weigh 18 lb. A gram-mole
of carbon dioxide would weigh 44 g. This appendix uses U.S. customary units for the
examples; therefore, only pound-moles will be used.
The product of the number of moles (n) and the molecular weight (MW) is equal
to the mass (m):
m n MW
n m/MW
Because molecular weight is the same as the number of pounds in a pound-mole:
lb lb-mole (lb/lb-mole)
lb-mole lb/(lb/lb-mole) (note that 1 lb/lb mole 1 g/g-mol)
TABLE A.3 Molecular weights of common diatomic gases.
Gas Abbreviation Molecular weight
Hydrogen H 2.016 ( 2)
2
Oxygen O 32.00 ( 32)
2
Nitrogen N 28.01 ( 28)
2