Page 323 - Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
P. 323
284 Wastewater Solids Incineration Systems
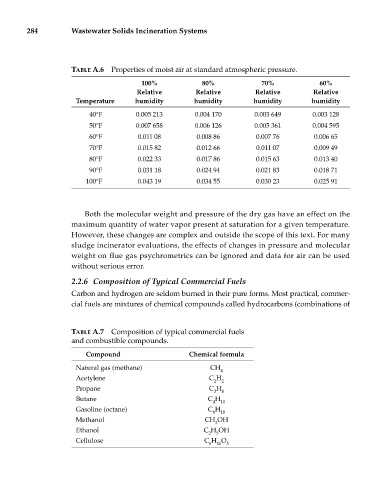
TABLE A.6 Properties of moist air at standard atmospheric pressure.
100% 80% 70% 60%
Relative Relative Relative Relative
Temperature humidity humidity humidity humidity
40°F 0.005 213 0.004 170 0.003 649 0.003 128
50°F 0.007 658 0.006 126 0.005 361 0.004 595
60°F 0.011 08 0.008 86 0.007 76 0.006 65
70°F 0.015 82 0.012 66 0.011 07 0.009 49
80°F 0.022 33 0.017 86 0.015 63 0.013 40
90°F 0.031 18 0.024 94 0.021 83 0.018 71
100°F 0.043 19 0.034 55 0.030 23 0.025 91
Both the molecular weight and pressure of the dry gas have an effect on the
maximum quantity of water vapor present at saturation for a given temperature.
However, these changes are complex and outside the scope of this text. For many
sludge incinerator evaluations, the effects of changes in pressure and molecular
weight on flue gas psychrometrics can be ignored and data for air can be used
without serious error.
2.2.6 Composition of Typical Commercial Fuels
Carbon and hydrogen are seldom burned in their pure forms. Most practical, commer-
cial fuels are mixtures of chemical compounds called hydrocarbons (combinations of
TABLE A.7 Composition of typical commercial fuels
and combustible compounds.
Compound Chemical formula
Natural gas (methane) CH
4
Acetylene C H
2 2
Propane C H
3 8
Butane C H
4 10
Gasoline (octane) C H
8 18
Methanol CH OH
3
Ethanol C H OH
2 5
Cellulose C H O
6 10 5