Page 268 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 268
246
Pumping, Storage, and Dual Water Systems
Chapter 8
2
falls past the point of maximum efficiency, normal discharge,
H = p ∕ + v ∕2g − p ∕ , where p ∕ is the absolute
sv
s
w
s
s
or rated capacity of the pump (point 1 in Fig. 8.4), the power
pressure, v is the velocity of the water in the inlet pipe,
s
continues to rise. If a centrifugal pump is operated against too
and p is the vapor pressure of the water pumped, with
w
low a head, a motor selected to operate the pump in the head
being the specific weight of water and g the gravity constant.
range around maximum efficiency may be overloaded. Pump
The energy grade line is at a distance h = p ∕ − p ∕ +
a
s
s
2
delivery can be regulated (a) by a valve on the discharge line,
v ∕2g from the eye of the impeller to the head delivered
s
(b) by varying the pump speed mechanically or electrically,
by the pump, where p is the atmospheric pressure. The
a
or (c) by throwing two or more pumps in and out of service
ratio H ∕h , where h = p ∕ − h , is called the cavitation
s
a
s
sv
to best advantage.
parameter.
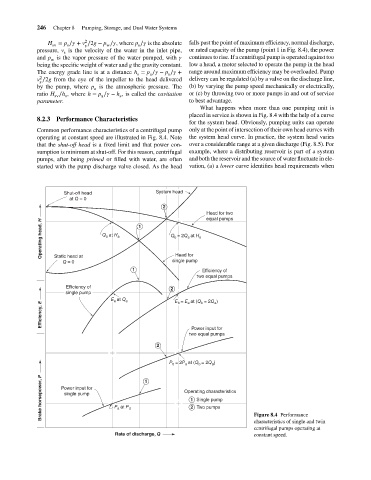
What happens when more than one pumping unit is
placed in service is shown in Fig. 8.4 with the help of a curve
8.2.3 Performance Characteristics
for the system head. Obviously, pumping units can operate
Common performance characteristics of a centrifugal pump only at the point of intersection of their own head curves with
operating at constant speed are illustrated in Fig. 8.4. Note the system head curve. In practice, the system head varies
that the shut-off head is a fixed limit and that power con- over a considerable range at a given discharge (Fig. 8.5). For
sumption is minimum at shut-off. For this reason, centrifugal example, where a distributing reservoir is part of a system
pumps, after being primed or filled with water, are often and both the reservoir and the source of water fluctuate in ele-
started with the pump discharge valve closed. As the head vation, (a) a lower curve identifies head requirements when
Shut-off head System head
at Q = 0
2
Head for two
equal pumps
Operating head, H Q a at H a 1 Q b = 2Q a at H a
Head for
Static head at
Q = 0 single pump
1 Efficiency of
two equal pumps
Efficiency of 2
single pump
E a at Q a E b = E a at (Q b = 2Q a )
Efficiency, E
Power input for
two equal pumps
2
P b = 2P a at (Q b = 2Q a )
Brake horsepower, P Power input for P a at P d 1 Operating characteristics
single pump
Single pump
1
Two pumps
2
Figure 8.4 Performance
characteristics of single and twin
centrifugal pumps operating at
Rate of discharge, Q constant speed.