Page 32 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 32
10
Chapter 1
Introduction to Water Systems
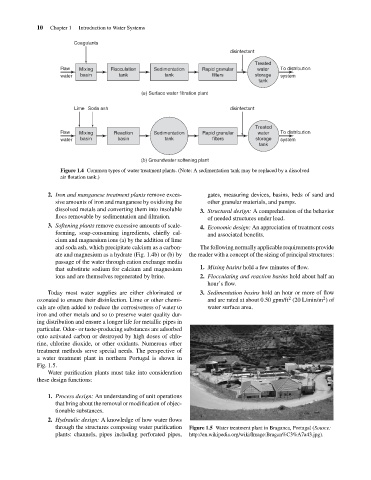
Coagulants
disinfectant
Treated
Raw
Flocculation
Mixing
water
Rapid granular
Sedimentation
storage
filters
tank
basin
tank
system
water
tank
(a) Surface water filtration plant
disinfectant
Lime Soda ash
Treated To distribution
Raw Mixing Reaction Sedimentation Rapid granular water To distribution
water basin basin tank filters storage system
tank
(b) Groundwater softening plant
Figure 1.4 Common types of water treatment plants. (Note: A sedimentation tank may be replaced by a dissolved
air flotation tank.)
2. Iron and manganese treatment plants remove exces- gates, measuring devices, basins, beds of sand and
sive amounts of iron and manganese by oxidizing the other granular materials, and pumps.
dissolved metals and converting them into insoluble 3. Structural design: A comprehension of the behavior
flocs removable by sedimentation and filtration. of needed structures under load.
3. Softening plants remove excessive amounts of scale- 4. Economic design: An appreciation of treatment costs
forming, soap-consuming ingredients, chiefly cal- and associated benefits.
cium and magnesium ions (a) by the addition of lime
and soda ash, which precipitate calcium as a carbon- The following normally applicable requirements provide
ate and magnesium as a hydrate (Fig. 1.4b) or (b) by the reader with a concept of the sizing of principal structures:
passage of the water through cation exchange media
that substitute sodium for calcium and magnesium 1. Mixing basins hold a few minutes of flow.
ions and are themselves regenerated by brine. 2. Flocculating and reaction basins hold about half an
hour’s flow.
Today most water supplies are either chlorinated or 3. Sedimentation basins hold an hour or more of flow
2
2
ozonated to ensure their disinfection. Lime or other chemi- and are rated at about 0.50 gpm/ft (20 L/min/m )of
cals are often added to reduce the corrosiveness of water to water surface area.
iron and other metals and so to preserve water quality dur-
ing distribution and ensure a longer life for metallic pipes in
particular. Odor- or taste-producing substances are adsorbed
onto activated carbon or destroyed by high doses of chlo-
rine, chlorine dioxide, or other oxidants. Numerous other
treatment methods serve special needs. The perspective of
a water treatment plant in northern Portugal is shown in
Fig. 1.5.
Water purification plants must take into consideration
these design functions:
1. Process design: An understanding of unit operations
that bring about the removal or modification of objec-
tionable substances.
2. Hydraulic design: A knowledge of how water flows
through the structures composing water purification Figure 1.5 Water treatment plant in Braganca, Portugal (Source:
plants: channels, pipes including perforated pipes, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Bragan%C3%A7a43.jpg).