Page 310 - Water Loss Control
P. 310
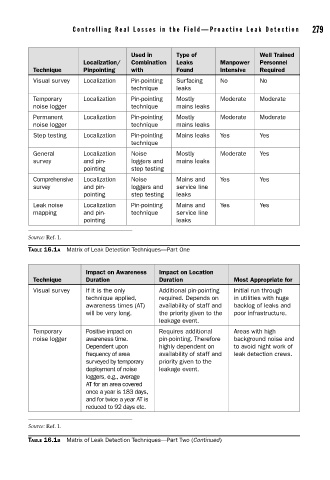
Contr olling Real Losses in the Field—Pr oactive Leak Detection 279
Used in Type of Well Trained
Localization/ Combination Leaks Manpower Personnel
Technique Pinpointing with Found Intensive Required
Visual survey Localization Pin-pointing Surfacing No No
technique leaks
Temporary Localization Pin-pointing Mostly Moderate Moderate
noise logger technique mains leaks
Permanent Localization Pin-pointing Mostly Moderate Moderate
noise logger technique mains leaks
Step testing Localization Pin-pointing Mains leaks Yes Yes
technique
General Localization Noise Mostly Moderate Yes
survey and pin- loggers and mains leaks
pointing step testing
Comprehensive Localization Noise Mains and Yes Yes
survey and pin- loggers and service line
pointing step testing leaks
Leak noise Localization Pin-pointing Mains and Yes Yes
mapping and pin- technique service line
pointing leaks
Source: Ref. 1.
TABLE 16.1A Matrix of Leak Detection Techniques—Part One
Impact on Awareness Impact on Location
Technique Duration Duration Most Appropriate for
Visual survey If it is the only Additional pin-pointing Initial run through
technique applied, required. Depends on in utilities with huge
awareness times (AT) availability of staff and backlog of leaks and
will be very long. the priority given to the poor infrastructure.
leakage event.
Temporary Positive impact on Requires additional Areas with high
noise logger awareness time. pin-pointing. Therefore background noise and
Dependent upon highly dependent on to avoid night work of
frequency of area availability of staff and leak detection crews.
surveyed by temporary priority given to the
deployment of noise leakage event.
loggers, e.g., average
AT for an area covered
once a year is 183 days,
and for twice a year AT is
reduced to 92 days etc.
Source: Ref. 1.
TABLE 16.1B Matrix of Leak Detection Techniques—Part Two (Continued)