Page 314 - Water Loss Control
P. 314
Contr olling Real Losses in the Field—Pr oactive Leak Detection 283
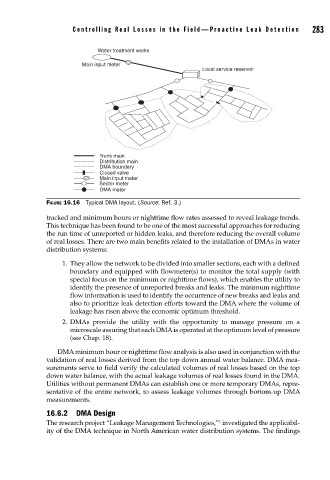
Water treatment works
Main input meter
Local service reservoir
Trunk main
Distribution main
DMA boundary
Closed valve
Main input meter
Sector meter
DMA meter
FIGURE 16.16 Typical DMA layout. (Source: Ref. 3.)
tracked and minimum hours or nighttime flow rates assessed to reveal leakage trends.
This technique has been found to be one of the most successful approaches for reducing
the run time of unreported or hidden leaks, and therefore reducing the overall volume
of real losses. There are two main benefits related to the installation of DMAs in water
distribution systems:
1. They allow the network to be divided into smaller sections, each with a defined
boundary and equipped with flowmeter(s) to monitor the total supply (with
special focus on the minimum or nighttime flows), which enables the utility to
identify the presence of unreported breaks and leaks. The minimum nighttime
flow information is used to identify the occurrence of new breaks and leaks and
also to prioritize leak detection efforts toward the DMA where the volume of
leakage has risen above the economic optimum threshold.
2. DMAs provide the utility with the opportunity to manage pressure on a
microscale assuring that each DMA is operated at the optimum level of pressure
(see Chap. 18).
DMA minimum hour or nighttime flow analysis is also used in conjunction with the
validation of real losses derived from the top down annual water balance. DMA mea-
surements serve to field verify the calculated volumes of real losses based on the top
down water balance, with the actual leakage volumes of real losses found in the DMA.
Utilities without permanent DMAs can establish one or more temporary DMAs, repre-
sentative of the entire network, to assess leakage volumes through bottom-up DMA
measurements.
16.6.2 DMA Design
1
The research project “Leakage Management Technologies,” investigated the applicabil-
ity of the DMA technique in North American water distribution systems. The findings