Page 227 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 227
6-4 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
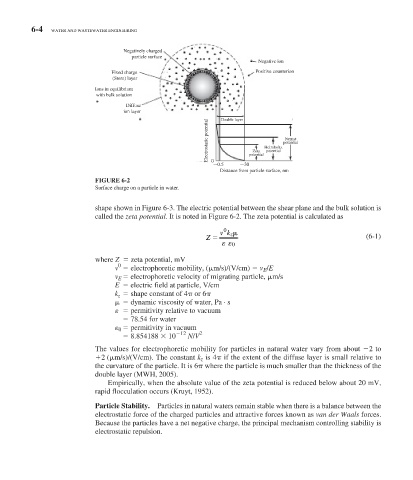
Negatively charged
particle surface
Negative ion
Fixed charge Positive counterion
(Stern) layer
Ions in equilibrium
with bulk solution
Diffuse
ion layer Double layer
Electrostatic potential Zeta Helmholtz potential
Nernst
potential
0
0.5 30 potential
Distance from particle surface, nm
FIGURE 6-2
Surface charge on a particle in water.
shape shown in Figure 6-3 . The electric potential between the shear plane and the bulk solution is
called the zeta potential. It is noted in Figure 6-2 . The zeta potential is calculated as
0
vkz
Z (6-1)
0
where Z zeta potential, mV
0
v electrophoretic mobility, (
m/s)/(V/cm) v E / E
v E electrophoretic velocity of migrating particle,
m/s
E electric field at particle, V/cm
k z shape constant of 4 or 6
dynamic viscosity of water, Pa · s
permitivity relative to vacuum
78.54 for water
0 permitivity in vacuum
2
8.854188 10 12 N / V
The values for electrophoretic mobility for particles in natural water vary from about 2 to
2 (
m/s)/(V/cm). The constant k z is 4 if the extent of the diffuse layer is small relative to
the curvature of the particle. It is 6 where the particle is much smaller than the thickness of the
double layer (MWH, 2005).
Empirically, when the absolute value of the zeta potential is reduced below about 20 mV,
rapid flocculation occurs (Kruyt, 1952).
Particle Stability. Particles in natural waters remain stable when there is a balance between the
electrostatic force of the charged particles and attractive forces known as van der Waals forces.
Because the particles have a net negative charge, the principal mechanism controlling stability is
electrostatic repulsion.